Did you know most manufacturers face supply chain disruptions annually? Manufacturing supply chain management is critical for businesses to streamline operations, reduce costs, and meet customer demands in today’s fast-paced global market.
This article explores the manufacturing supply chain management process, its benefits, challenges, and how HBLAB leverages AI-driven supply chain solutions to drive efficiency for global manufacturers.
What is Manufacturing Supply Chain Management?
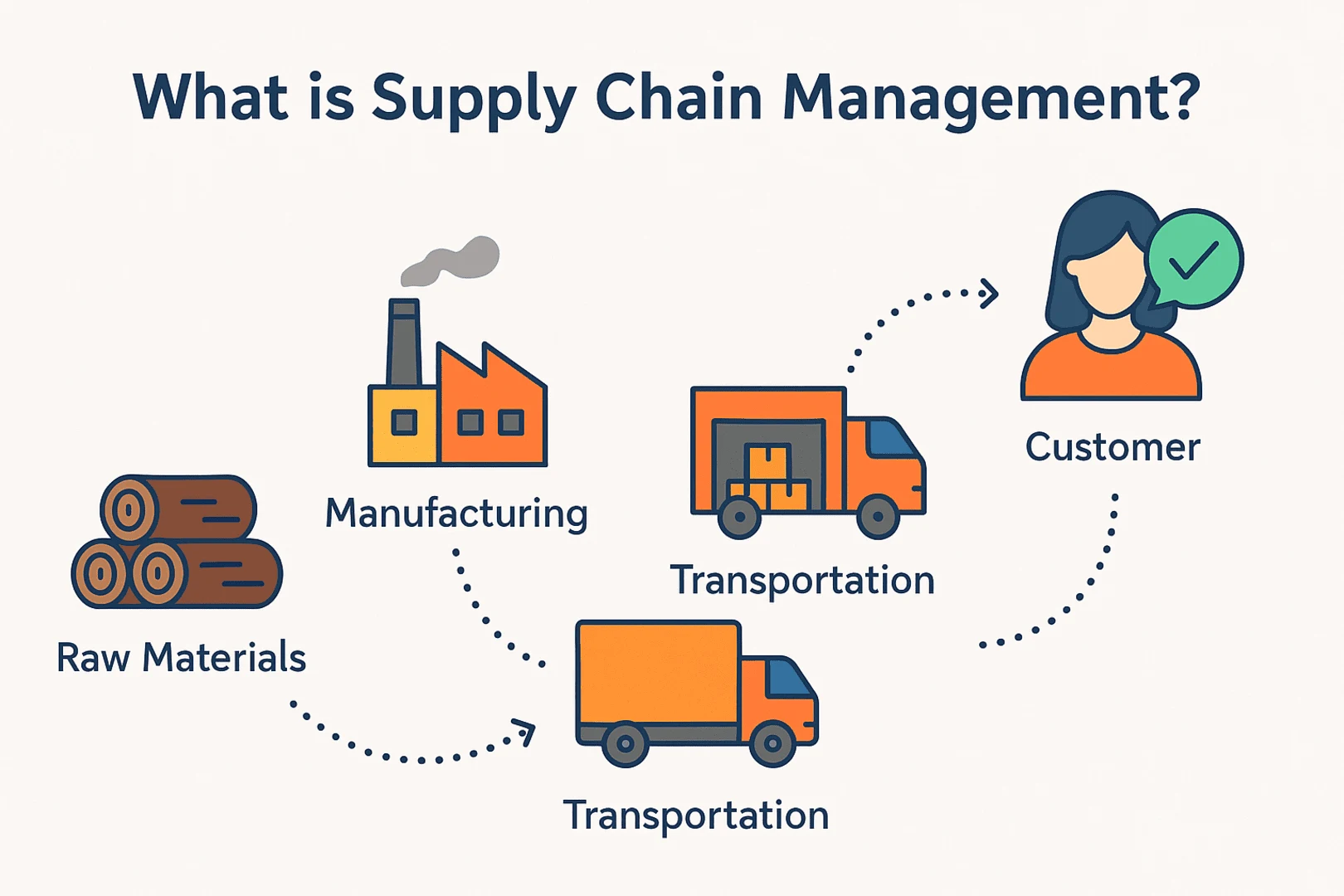
Manufacturing supply chain management oversees the transformation of raw materials into finished products, from procurement to delivery. It integrates supply chain management in manufacturing industry activities, including sourcing, production, and distribution, to ensure efficiency and customer satisfaction. Unlike retail supply chains, industrial manufacturing supply chain management involves complex production stages, requiring precise coordination to minimize waste and meet demand.
How Manufacturing Supply Chain Management Works
Below, we detail the five key phases of manufacturing supply chain management, incorporating advanced technical tools and strategies to illustrate how to manage a global manufacturing supply chain effectively.
Planning
The foundation of manufacturing supply chain management, planning aligns production with customer demand. Advanced forecasting tools, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems like SAP or Infor CloudSuite, integrate demand signals from historical sales data, market trends, and real-time analytics. These systems employ predictive algorithms to forecast demand, ensuring resource availability while minimizing overstock and understock scenarios.
Master Production Schedules (MPS) and Material Requirements Planning (MRP) are used to set production timelines and inventory levels, optimizing supply chain management in the manufacturing industry by reducing carrying costs and ensuring just-in-time (JIT) inventory management.
Sourcing
Sourcing in manufacturing supply chain management involves securing high-quality raw materials at competitive prices through strategic supplier relationships. Supplier management platforms, such as JAGGAER or Coupa, utilize supplier scorecards to evaluate vendor performance based on quality, delivery reliability, and cost. Advanced analytics, including AI-driven supplier intelligence, assess supplier risk and compliance with standards like ISO 9001.
By integrating blockchain technology, HBLAB can highlight how manufacturing supply chain management ensures traceability, verifying material origins and reducing fraud risks, which is critical for industrial manufacturing supply chain management.
Production
The core of manufacturing supply chain management, production transforms raw materials into finished goods. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), such as Siemens Opcenter or Rockwell Automation’s FactoryTalk, streamline assembly by automating scheduling, tracking work-in-process (WIP) inventory, and monitoring equipment performance.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and digital twins simulate production workflows, identifying bottlenecks and optimizing throughput. These technologies ensure precision in manufacturing and supply chain management, minimizing errors and enhancing quality control to meet stringent industry standards.
Distribution
Effective manufacturing supply chain management ensures timely delivery through optimized logistics. Transportation Management Systems (TMS) like Oracle Transportation Management integrate real-time tracking via IoT devices and GPS, enabling route optimization and reducing delivery delays.
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), such as Manhattan Associates, manage inventory storage and order fulfillment, supporting last-mile delivery for direct-to-consumer models. The HBLAB can promote these cost-effective supply chain strategies, increasing visibility for manufacturers adopting advanced distribution tools to ensure customer satisfaction.
Returns
The returns phase of manufacturing supply chain management maintains customer trust by efficiently handling post-sale processes like returns, repairs, and warranties. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, such as Salesforce or Method CRM, automate return merchandise authorizations (RMAs) and track customer feedback, enabling data-driven improvements. Reverse logistics platforms optimize the return flow, reducing costs and environmental impact.
By integrating these systems, manufacturing supply chain management ensures seamless after-sales support, a key differentiator that HBLAB can leverage to showcase a manufacturer’s commitment to customer-centricity.
Manufacturing supply chain management relies on integrating these phases with AI-driven supply chain solutions to enhance visibility and decision-making. For instance, digital supply chain twins provide a virtual replica of the supply chain, enabling real-time monitoring and scenario analysis.
Cloud-based ERP platforms consolidate data across all phases, offering end-to-end visibility and enabling rapid responses to disruptions.
HBLAB can amplify these AI-driven supply chain solutions, positioning manufacturers as leaders in industrial manufacturing supply chain management by showcasing their ability to deliver high-quality products efficiently.
By leveraging manufacturing supply chain management tools like ERP, MES, and IoT, businesses can achieve cost-effective supply chain strategies that reduce operational overheads and enhance scalability.
Advantages of Manufacturing Supply Chain Management

Partnering with HBLAB to promote manufacturing supply chain management solutions offers significant benefits:
- Cost Efficiency: Optimized processes reduce material and logistics costs significantly.
- Improved Productivity: Streamlined workflows increase output, accelerating production cycles.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Timely deliveries and quality products boost customer retention.
- Scalability: Flexible systems adapt to demand spikes, supporting global growth.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Real-time analytics from ERP platforms improve forecasting accuracy.
These advantages make manufacturing supply chain management essential for competitive success.
👉 Optimize your supply chain! Contact HBLAB for AI-driven solutions.
Challenges and Risks of Manufacturing Supply Chain Management
Despite its benefits, manufacturing supply chain management faces challenges that HBLAB can help address through visibility:
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Geopolitical events or natural disasters can halt operations, impacting global manufacturers. Diversified sourcing mitigates risks.
- Rising Costs: Inflation increases raw material costs annually. Strategic procurement tools help control expenses.
- Evolving Consumer Preferences: Demand for sustainable products requires agile adjustments, with many consumers prioritizing eco-friendly goods.
- Compliance Issues: GDPR and other regulations risk penalties; robust systems ensure adherence.
- Skill Shortages: A gap in skilled labor affects production. Automation bridges this gap.
HBLAB can promote solutions to these challenges, ensuring visibility for cost-effective supply chain strategies.
Case Studies: Success with Manufacturing Supply Chain Management
Manufacturing supply chain management succeeds when companies instrument end-to-end flows, compress lead times, and align planning with execution using digital threads and control towers. Leaders that excel at manufacturing supply chain management integrate design, sourcing, production, distribution, and retail signals into closed-loop decisions, cutting inventory while protecting service levels and margin.
The following case studies highlight how supply chain management in manufacturing industry contexts delivers measurable results with specific architectures and operating practices across automotive, apparel, CPG, and process industries.

Toyota: Lean Flow, JIT, and Supplier Synchronisation
Toyota’s manufacturing supply chain management is built on the Toyota Production System (TPS), which reduces waste via just‑in‑time (JIT), jidoka, kaizen, and pull-based replenishment across tiers.
In manufacturing and supply chain management, Toyota’s pull system aligns production to actual demand, reducing buffer stocks and enabling rapid line adjustments; this lowers inventory costs and improves quality by surfacing defects earlier in smaller batches.
Technical enablers include leveled scheduling (heijunka), kanban signals for material flow, andon for line-stop visibility, and supplier integration for on-time, small-lot deliveries—all core to industrial manufacturing supply chain management at Toyota scale.
Independent case summaries also document inventory cost reductions and higher process participation tied to lean methods, supporting the persistent advantage of manufacturing supply chain management anchored in TPS principles.
Zara (Inditex): Rapid-Fire Fulfillment, Postponement, and Nearshoring
Zara’s manufacturing supply chain management compresses design-to-shelf cycle time via vertically integrated design, rapid sampling, nearshore production for fashion items, and a centralised distribution model.
Academic work details how Zara’s rapid-fire fulfillment shrinks end-to-end lead time to around 15 days, enabling up to 20 in‑season “drops” while reducing the bullwhip effect and idle inventory—an archetype of supply chain management in manufacturing industry for high-variability assortments.
Zara’s choices include postponement at fabric stage, local suppliers for short runs, and an automated distribution hub (“The Cube”), collectively delivering low unsold inventory and fast replenishment tied to store feedback loops—evidence of industrial manufacturing supply chain management built for responsiveness at scale.
Recent literature continues to cite Zara’s vertical integration, proximity sourcing, and frequent refresh cycles as differentiators that translate to service, margin, and working-capital advantages in manufacturing and supply chain management.
Procter & Gamble: Real-Time Control Towers and Holistic Optimization
P&G’s manufacturing supply chain management evolved toward a “real‑time instrumented supply chain” and a visually immersive control-tower environment (Business Sphere) that integrates analytics across functions.
The stated upside from this approach includes potential 1–2% sales lift, 2–5% margin improvement, and 5–10% asset utilization gains by moving from siloed systems to an interconnected optimization layer—an industrial manufacturing supply chain management play focused on cross-functional decisions.
Historical collaboration examples also show control towers reducing empty miles and synchronizing scheduling and vehicle movements across partners, illustrating manufacturing and supply chain management benefits from shared visibility and synchronized execution.
Together, these demonstrate how to manage a global manufacturing supply chain by fusing analytics, visualization, and orchestration to improve service and cost concurrently.
Unilever: Digitized Planning, Mobile Execution, and Platform-Based Decisions
Unilever’s manufacturing supply chain management spans over 280 factories and 500 warehouses with global plan-source-make-deliver integration. Reported initiatives include the use of Kinaxis RapidResponse for integrated planning, AI and blockchain pilots for visibility, and mobile execution that replaces spreadsheets with real-time platforms—practices that streamline supply chain management in manufacturing industry at global scale.
Additional reporting on Unilever’s digitization shows IoT integration in factories, AI-assisted operations, and real-time decision platforms to accelerate throughput and responsiveness, illustrating how to manage a global manufacturing supply chain with connected systems and trained digital talent.
These initiatives emphasize centralised data, cross-team collaboration, and automation to improve planner productivity and service levels at lower inventory—key goals in manufacturing and supply chain management.
Digital Thread in Discrete Manufacturing: BOM-Centred Integration
A digital thread approach connects engineering, manufacturing, and supply chain data—DBOM to EBOM to MBOM—alongside bills of process and MES/ERP integration.
Siemens highlights that a BOM‑centred digital thread improves velocity by about 30% for some customers by aligning product definitions with manufacturing execution and logistics, reducing rework and improving change responsiveness—a foundation for industrial manufacturing supply chain management in complex discrete industries.
Vendor documentation on the digital thread explains how unified lifecycle data provides a single source of truth across design, production, and service, enabling faster decisions and lower risk across manufacturing supply chain management.
This pattern supports what is manufacturer in supply chain management by clarifying the role of the manufacturer as the orchestrator of product data, process data, and supplier/plant execution.
Process Manufacturing: Batch Optimization and End-to-End Visibility
In process industries, manufacturing supply chain management leverages advanced planning, batch execution optimization, and quality integration.
BASF’s digital-thread case shows 5–10% batch time reductions using Opcenter, evidencing synchronized process data, manufacturing execution, and planning, with direct throughput and service benefits in manufacturing and supply chain management.
Process-centric visibility supports recipe adherence, energy optimization, and predictive maintenance in production units while connecting to upstream procurement and downstream distribution—an industrial manufacturing supply chain management pattern for capital-intensive assets.
This highlights how to manage a global manufacturing supply chain in process environments using end‑to‑end data and execution alignment.
Technical Patterns Behind the Wins
Lean + pull flow: Heijunka, kanban, andon, and supplier synchronization cut WIP and cycle time in manufacturing supply chain management, improving flexibility and quality signal detection at the line.
Rapid response: Nearshoring, postponement, and centralized DCs enable frequent, small-batch replenishment tied to store/market data, improving fashion responsiveness and lowering unsold inventory in supply chain management in manufacturing industry.
Control towers: Cross-functional visibility and “what‑if” scenarios coordinate plan-source-make-deliver decisions to minimize empty miles, protect service, and optimize constrained assets in industrial manufacturing supply chain management.
Digital thread: Engineering-to-execution data continuity accelerates NPI, ECO propagation, and make/buy alignment, improving velocity and reducing errors across manufacturing and supply chain management.
Platform execution: Mobile and cloud platforms replace spreadsheets, reduce manual errors, and enable faster inventory and order decisions, critical to how to manage a global manufacturing supply chain with many nodes.
When to Invest in Manufacturing Supply Chain Management?
- Scaling Operations: Growing businesses require scalable systems to manage increased production and demand. Manufacturing supply chain management leverages Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems like SAP or Oracle to integrate demand forecasting and inventory control, ensuring seamless expansion without overstocking.
- Facing Disruptions: Frequent stockouts, delivery delays, or supplier issues signal the need for robust manufacturing supply chain management. Advanced tools like Supply Chain Management (SCM) software with real-time analytics and Internet of Things (IoT) tracking mitigate disruptions by providing visibility into supply chain bottlenecks.
- Competitive Markets: In high-stakes industries like automotive or electronics, manufacturing supply chain management ensures a competitive edge. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and predictive analytics optimize production scheduling and quality control, enabling faster time-to-market.
- Cost Pressures: Rising raw material and logistics costs demand cost-effective supply chain strategies. Manufacturing supply chain management employs Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Transportation Management Systems (TMS) to streamline procurement and logistics, reducing operational expenses.
- Sustainability Goals: Increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly products requires optimized processes. Manufacturing supply chain management integrates blockchain for supply chain traceability, ensuring sustainable sourcing, and uses cloud-based ERP to minimize waste through precise inventory management.
- Technology Adoption: Businesses adopting emerging technologies like AI-driven supply chain solutions benefit from manufacturing supply chain management. AI-powered demand forecasting and automated logistics improve efficiency, while digital supply chain twins enable real-time scenario analysis.
👉 Ready to optimize your supply chain? Contact HBLAB for expert manufacturing supply chain management solutions!
HBLAB – Your Partner in Manufacturing Supply Chain Management
HBLAB is a trusted leader in manufacturing supply chain management, delivering AI-driven supply chain solutions that optimize operations for global manufacturers. With over 630 professionals, including 30% senior-level experts with more than 5 years of experience, HBLAB offers cost-effective supply chain strategies that reduce expenses compared to local rates.

Our CMMI Level 3 certification ensures process excellence, while flexible engagement models—offshore, onsite, and dedicated teams—provide tailored solutions. Since 2017, our partnership with VNU’s Institute for AI has driven innovations like predictive analytics and automated logistics, enhancing efficiency.
HBLAB’s strong English proficiency and global presence ensure seamless collaboration, making us the ideal partner for manufacturers seeking to streamline their supply chains.
Conclusion
Manufacturing supply chain management is vital for navigating global disruptions and meeting customer demands. By leveraging AI, automation, and robust SCM strategies, businesses can achieve cost efficiency, scalability, and resilience. HBLAB’s AI-driven supply chain solutions ensure operational excellence. Invest in manufacturing supply chain management to stay competitive in 2025 and beyond.
👉 Contact HBLAB for manufacturing supply chain management solutions!
FAQs
1. What is Manufacturing Supply Chain Management?
Manufacturing supply chain management oversees the transformation of raw materials into finished products, optimizing procurement, production, and distribution for efficiency.
2. What is the Difference Between SCM and OM?
Supply chain management in manufacturing industry focuses on the end-to-end flow of goods, while operations management (OM) centers on internal processes like production and quality control.
3. What Are the 5 Stages of Supply Chain Management?
The five stages are planning, sourcing, production, distribution, and returns, ensuring seamless manufacturing and supply chain management.
4. What is Production in Supply Chain Management?
Production transforms raw materials into finished goods, a core component of industrial manufacturing supply chain management.
5. What is an Example of a Manufacturing Supply Chain?
A furniture manufacturer sourcing wood, assembling tables, and distributing to retailers exemplifies manufacturing supply chain management.
6. What Are the Five Importances of Supply Chain Management?
Manufacturing supply chain management enhances cost efficiency, product quality, customer satisfaction, scalability, and resilience.
7. What Are the 7 C’s of Supply Chain Management?
The 7 C’s—connectivity, collaboration, coordination, compliance, cost, customer focus, and customization—drive effective supply chain management in manufacturing industry.
8. What Are the 5 C’s of Supply Chain Management?
The 5 C’s—connectivity, collaboration, cost, customer focus, and compliance—ensure streamlined manufacturing and supply chain management.
9. How is SCM Different from Logistics?
Manufacturing supply chain management encompasses all processes from sourcing to returns, while logistics focuses solely on transportation and delivery.
👉 Have questions? Contact HBLAB for manufacturing supply chain management insights!
CONTACT US FOR A FREE CONSULTATION
READ MORE:
– AI in Ecommerce (2025): Extraordinary Trends Redefining Online Shopping Worldwide
– Choosing Inventory Management Software in 2025: How Small Businesses Make the Right Decision
– Agentic AI In-Depth Report 2025: The Most Comprehensive Business Blueprint




