Did you know that 96% of US hospitals and 78% of office-based physicians have adopted EMR systems, transforming healthcare delivery worldwide?
Electronic Medical Record (EMR) systems have revolutionized how healthcare providers manage patient information, streamline operations, and deliver quality care in the digital age.
What is an EMR System?

Electronic Medical Record (EMR) systems are comprehensive digital platforms that store, manage, and retrieve patient health information electronically. An EMR system allows healthcare providers to create, gather, manage, and access patient records within a single healthcare organization, replacing traditional paper-based medical records with secure, interoperable digital solutions.
EMR systems contain essential patient data including:
• Patient Demographics: Name, address, contact information, insurance details
• Medical History: Previous diagnoses, treatments, surgical procedures
• Medications: Current prescriptions, dosages, allergies, drug interactions
• Laboratory Results: Blood work, imaging studies, diagnostic test results
• Clinical Notes: Provider observations, treatment plans, progress notes
• Vital Signs: Blood pressure, temperature, heart rate, weight measurements
Modern EMR systems serve as the digital backbone of healthcare delivery, enabling seamless data sharing, improved care coordination, and enhanced patient safety across various healthcare settings.
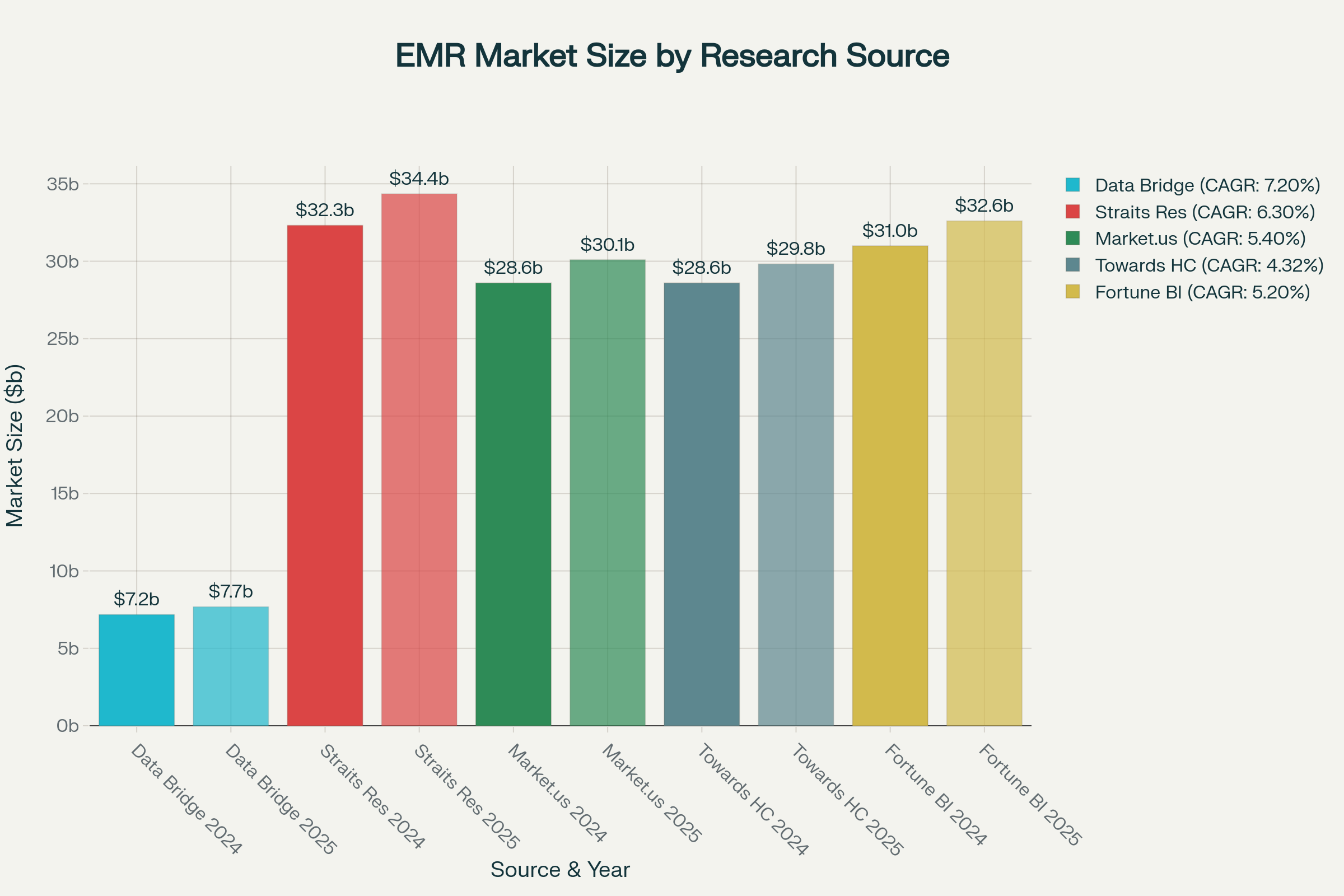
EMR Market Size Projections by Research Source (2024-2025)
How EMR Systems Work in Healthcare
EMR systems operate through integrated workflows that digitize every aspect of patient care documentation and management. The process begins with patient registration, where demographic and insurance information is captured electronically. Healthcare providers then document patient encounters, update treatment plans, and access historical data through intuitive interfaces designed for clinical workflows.
Key operational components include:
Data Entry and Documentation: Providers input patient information using standardized templates, dropdown menus, and voice recognition technology, ensuring consistency and completeness.
Clinical Decision Support: Built-in algorithms provide real-time alerts for drug interactions, allergy warnings, and evidence-based treatment recommendations.
Integration Capabilities: EMR systems connect with laboratory information systems, radiology platforms, pharmacy networks, and billing systems for seamless data exchange.
Security and Compliance: Advanced encryption, user authentication, and audit trails ensure HIPAA compliance and protect sensitive patient information.
The electronic health record process creates an interconnected cycle spanning assessment, nursing diagnosis, intervention, implementation, and evaluation stages, benefiting patients, healthcare providers, and administrative staff.
Key Features and Components of EMR Systems

Comprehensive EMR systems incorporate essential features that enhance clinical workflows and improve patient outcomes. According to the Institute of Medicine, EMR systems should support eight key functions for safety, quality, and care efficiency.
Patient Management
• Electronic patient registration and scheduling
• Comprehensive medical history tracking
• Demographic and insurance information management
• Patient portal access for engagement
Clinical Documentation
• Structured data entry with templates
• Progress notes and clinical observations
• Care plan development and management
• Quality measure tracking
Computerized Provider Order Entry (CPOE)
• Electronic prescription management
• Laboratory and radiology test ordering
• Medication dosage calculations
• Drug interaction warnings
Decision Support Tools
• Clinical guidelines and protocols
• Evidence-based treatment recommendations
• Risk assessment calculators
• Preventive care reminders
Interoperability Standards
• HL7 FHIR compliance for data exchange
• Integration with external systems
• Data sharing across healthcare networks
• Standardized terminology support
Reporting and Analytics
• Population health management
• Quality metrics and performance indicators
• Regulatory compliance reporting
• Financial and operational analytics
Advantages of EMR Systems
EMR systems deliver substantial benefits to healthcare organizations, providers, and patients through improved efficiency, enhanced care quality, and cost optimization. Research demonstrates that healthcare organizations implementing advanced EMR systems achieve significant operational and clinical improvements.
Enhanced Patient Care and Safety
EMR systems significantly improve patient outcomes through better care coordination and error reduction. Studies show that EMR implementation leads to:
• 17.5% reduction in medical errors through automated alerts and decision support
• Improved medication safety with drug interaction warnings and allergy alerts
• Enhanced care coordination through seamless information sharing among providers
• Better chronic disease management with automated reminders and tracking
Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings
Financial benefits of EMR implementation are substantial, with healthcare organizations realizing positive return on investment within months of deployment:
• Average cost savings of $731 per patient admission (9.66% reduction) in hospitals with advanced EMR systems
• Net benefit of $86,400 per provider over a five-year period
• Administrative cost reduction up to $42,500 per provider annually
• Break-even period of approximately 10 months for primary care practices
Improved Documentation and Compliance
EMR systems enhance documentation quality and regulatory compliance through:
• Standardized documentation processes reducing variability and errors
• Automated compliance reporting for quality measures and regulatory requirements
• Comprehensive audit trails for security and accountability
• Reduced transcription costs and paper-based administrative expenses
Better Patient Engagement
Patient-centered features improve healthcare experiences and outcomes:
• Patient portal access for viewing records and communicating with providers
• Appointment scheduling and prescription refill capabilities
• Health information resources and educational materials
• Improved patient satisfaction through reduced wait times and better communication
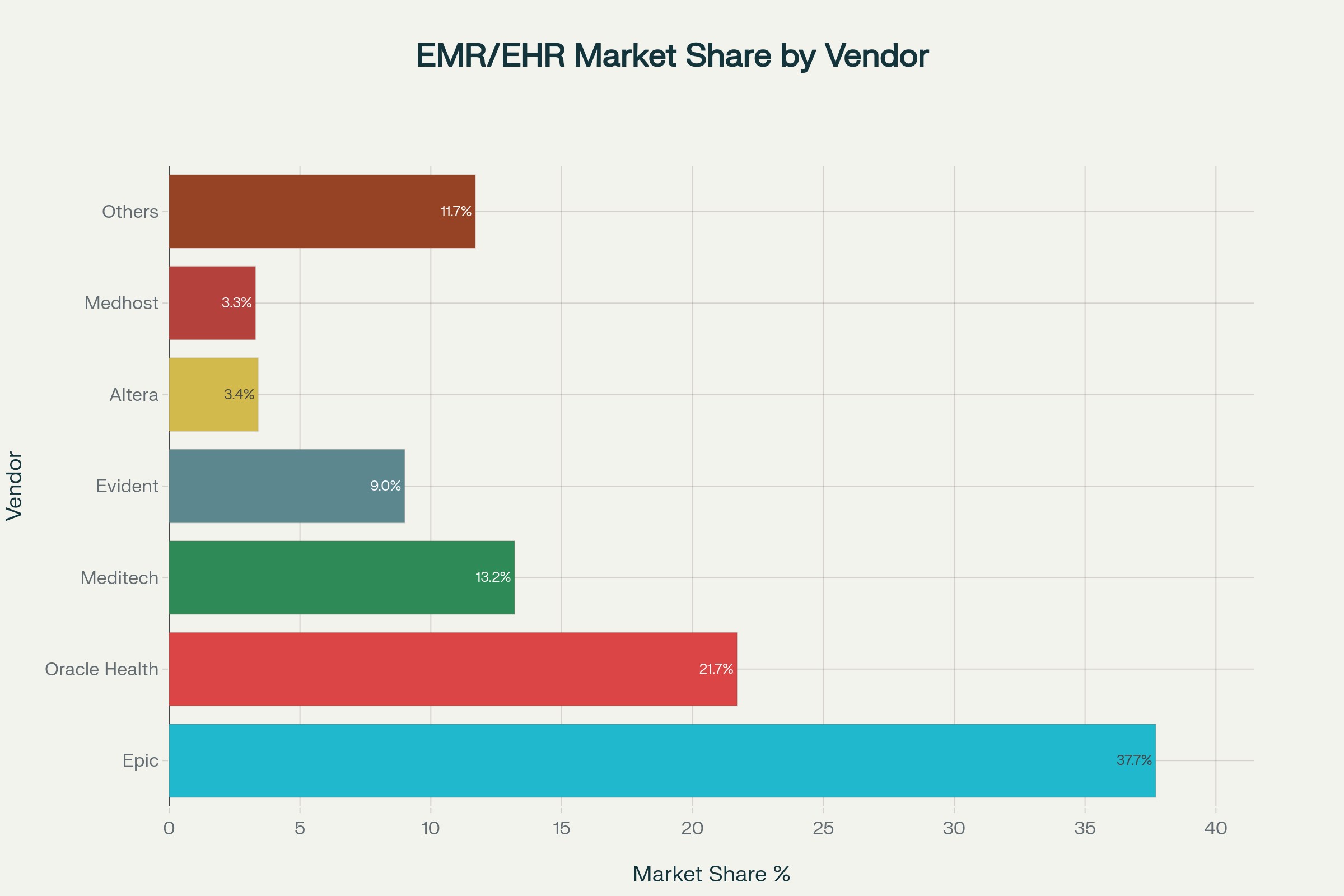
Hospital EMR/EHR Market Share by Vendor (2024)
Challenges and Risks of EMR Implementation
EMR implementation presents significant challenges that healthcare organizations must address to ensure successful adoption and meaningful use. Research identifies multiple barriers that can impact system effectiveness and user satisfaction.
🚀 Access valuable AI-driven IT strategy documents and transform your business today.
Technical and Infrastructure Challenges
System performance and integration issues commonly affect EMR implementations:
• System slowness affecting 45.5% of healthcare providers, impacting workflow efficiency
• Integration difficulties with legacy systems and third-party applications
• Network connectivity issues causing system downtime and access problems
• Hardware and software compatibility requiring significant infrastructure upgrades
User Adoption and Training Barriers
Healthcare provider resistance remains a persistent challenge in EMR deployments:
• 50.4% of providers report slow typing speeds affecting documentation efficiency
• 36.2% cite unfamiliarity with the system as a primary barrier
• Inadequate training and follow-up support affecting 38% of implementations
• Low user acceptance particularly during initial phases of deployment
Financial and Resource Constraints
Cost considerations represent significant barriers, especially for smaller practices:
• High initial implementation costs averaging $44,000 per provider
• Ongoing maintenance expenses of approximately $8,500 annually per provider
• Training and support costs often underestimated during planning phases
• Potential revenue disruption during transition periods
>>> Ready to transform your healthcare organization with cutting-edge EMR solutions?
Patient Care Impact
EMR systems can initially disrupt patient-provider interactions:
• 57.6% of providers report less eye contact with patients during consultations
• 42.7% cite longer waiting times for patient consultations
• 33.2% express concerns about patient privacy in digital systems
• 35.2% report unnecessary costs due to system-related errors
Security and Compliance Risks
Healthcare data security remains a critical concern with EMR systems:
• Average data breach cost of $9.23 million in healthcare, the highest among all industries
• EMR systems containing 18 HIPAA-protected identifiers, making them valuable targets for cybercriminals
• Potential for data loss or destruction during system failures or cyber attacks
• Regulatory compliance complexity requiring ongoing monitoring and updates
EMR vs EHR: Understanding the Difference
Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) and Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are often used interchangeably, but they serve different purposes in healthcare information management. Understanding these distinctions helps healthcare organizations choose appropriate solutions for their specific needs.
EMR System Characteristics
EMR systems are primarily designed for single healthcare organizations:
• Internal focus: Data remains within one healthcare facility or practice
• Provider-centric: Designed for specific clinical workflows and documentation needs
• Limited sharing capabilities: Data exchange typically restricted to internal departments
• Cost-effective: Generally less expensive for smaller healthcare facilities
EHR System Characteristics
EHR systems emphasize interoperability and comprehensive health information:
• Multi-organizational: Designed for data sharing across different healthcare providers
• Patient-centric: Comprehensive view of patient health across all care settings
• Advanced interoperability: Seamless data exchange with external providers and systems
• Population health focus: Support for public health reporting and population management
Choosing the Right System
Healthcare organizations should consider their specific requirements:
EMR systems are suitable for:
• Small to medium-sized practices
• Single-location healthcare facilities
• Organizations with limited interoperability needs
• Budget-conscious implementations
EHR systems are ideal for:
• Large healthcare systems and hospitals
• Multi-location healthcare organizations
• Providers requiring extensive data sharing capabilities
• Organizations focused on population health management
Top EMR Vendors and Market Share
The EMR market is dominated by several key vendors, with Epic Systems and Oracle Health (Cerner) holding the largest market shares. Understanding vendor positioning helps healthcare organizations make informed technology decisions.
Market Leadership
Epic Systems maintains the strongest market position:
• 37.7% market share in acute care hospitals
• Largest net gain of 74 hospitals in 2024
• 43.92% market share in ambulatory care settings
• Strong reputation for integration capabilities and customer satisfaction
Oracle Health (Cerner) holds the second position:
• 21.7% market share in acute care hospitals, down from 23.4%
• Net loss of 74 hospitals in 2024 following Oracle acquisition
• Strong government presence, particularly with VA contracts
• Focus on modernization following $28.3 billion Oracle acquisition
Established Vendors
Other significant market players include:
Meditech: 13.2% market share, focusing on community hospitals and integrated delivery networks
Evident (CPSI): 9% market share, serving rural and community hospitals
Altera Digital Health: 3.4% market share in specialized healthcare segments
Medhost: 3.3% market share with focus on acute care solutions
Market Consolidation Trends
The EMR market has become increasingly concentrated:
• Market concentration index exceeded 2,500 in 2018, indicating “highly concentrated” status
• Top two vendors (Epic and Oracle Health) control nearly 60% of the hospital market
• Vendor partnerships have emerged as key differentiators in market competition
• Acquisition activity continues to reshape competitive landscape
EMR Implementation Success Stories
Successful EMR implementations demonstrate the transformative potential of electronic health records when properly planned and executed. Healthcare organizations worldwide have achieved remarkable improvements in care quality, operational efficiency, and financial performance.
The Role of AI and Emerging Technologies
Artificial intelligence and emerging technologies are transforming EMR systems, creating intelligent healthcare platforms that enhance clinical decision-making and operational efficiency. The healthcare AI market is projected to grow from $9 billion in 2024 to over $200 billion by 2030.

AI-Powered Clinical Decision Support
Machine learning algorithms enhance EMR capabilities:
• Predictive analytics for early disease detection and risk stratification
• Clinical decision support providing evidence-based treatment recommendations
• Pattern recognition in diagnostic imaging and laboratory results
• Population health insights for preventive care initiatives
Ambient Documentation Technologies
Generative AI transforms clinical documentation:
• 100% adoption rate of ambient notes solutions among leading health systems
• High success rates with over 50% reporting significant benefits
• Reduced clinician burnout through automated documentation
• Improved workflow efficiency and productivity
Interoperability and Data Exchange
Advanced interoperability standards enable seamless data sharing:
• FHIR compliance facilitating API-based data exchange
• Cloud-native architectures supporting scalable integrations
• Real-time data synchronization across healthcare networks
• Patient-controlled data sharing through secure portals
Future Technology Trends
Emerging technologies shaping EMR evolution include:
• Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
• Remote patient monitoring integration with EMR systems
• Wearable device data incorporation into patient records
• Real-time vital sign monitoring and alerting
Blockchain Technology
• Secure data sharing across healthcare networks
• Patient data ownership and consent management
• Immutable audit trails for regulatory compliance
Advanced Analytics
• Precision medicine based on genomic and patient data
• Digital twins for treatment simulation and optimization
• Predictive modeling for resource planning and capacity management
When to Implement an EMR System
Healthcare organizations should prioritize EMR implementation when facing specific operational, regulatory, or competitive challenges. Strategic timing ensures maximum return on investment and successful adoption.
Operational Indicators
EMR implementation becomes critical when organizations experience:
Scalability Challenges
• Expanding to new locations or service lines requiring standardized workflows
• Growing patient volumes overwhelming paper-based systems
• Multi-site operations needing centralized patient information
Efficiency Bottlenecks
• Administrative burden consuming excessive staff time and resources
• Documentation delays affecting patient care and billing cycles
• Duplicate testing and redundant procedures due to information gaps
Quality and Safety Concerns
• Medical errors resulting from illegible handwriting or missing information
• Medication mistakes lacking automated safety checks
• Care coordination gaps between departments or providers
Regulatory and Compliance Drivers
Regulatory requirements often mandate EMR adoption:
• Meaningful Use incentives and penalties affecting reimbursement
• Quality reporting requirements demanding electronic data submission
• HIPAA compliance necessitating secure electronic records management
• State mandates requiring electronic health information infrastructure
Competitive and Strategic Factors
Market positioning may require EMR investment:
• Patient expectations for digital health services and portal access
• Provider recruitment challenges without modern technology infrastructure
• Payer relationships requiring electronic transactions and reporting
• Telemedicine capabilities demanding integrated digital records
Financial Readiness Indicators
Organizations should implement EMR systems when:
• Capital funding is available for initial investment of $44,000+ per provider
• Ongoing operational budgets can support annual costs of $8,500+ per provider
• Break-even expectations align with 10-month ROI timeline
• Cash flow stability can withstand temporary revenue disruption during implementation
Technology Infrastructure Assessment
EMR readiness requires adequate technical foundations:
• Network infrastructure supporting high-speed, reliable connectivity
• Hardware capabilities meeting system requirements and user demands
• IT support resources for implementation, training, and ongoing maintenance
• Security systems ensuring HIPAA compliance and data protection
HBLAB – Your Partner in EMR Development
HBLAB stands out as a trusted partner in healthcare software development, delivering innovative EMR solutions that transform patient care and operational efficiency. With over 10 years of experience in custom healthcare software development, HBLAB combines deep technical expertise with healthcare industry knowledge to create tailored EMR systems that meet the unique needs of healthcare organizations worldwide.

Healthcare Software Expertise
HBLAB’s healthcare specialization includes comprehensive EMR development capabilities:
• Custom EMR system development tailored to specific clinical workflows and requirements
• EHR modernization and integration connecting legacy systems with advanced digital platforms
• Interoperability solutions enabling seamless data exchange across healthcare networks
• AI-powered clinical decision support enhancing diagnostic accuracy and treatment recommendations
Technical Excellence and Quality Assurance
HBLAB delivers world-class healthcare technology solutions through proven methodologies:
• 630+ IT professionals with 30% senior-level expertise in complex healthcare projects
• CMMI Level 3 certification ensuring process excellence and quality management
• 10+ years of healthcare software experience from EHRs to AI-powered diagnostic tools
• Comprehensive security implementation with HIPAA/GDPR compliance and audit capabilities
Flexible Engagement Models
HBLAB adapts to diverse client requirements through multiple collaboration approaches:
• Offshore development teams providing cost-effective access to specialized talent
• Onsite collaboration for complex integrations and sensitive healthcare environments
• Dedicated team models offering long-term partnership and deep domain knowledge
• Hybrid engagement options combining offshore efficiency with local presence
AI and Innovation Leadership
HBLAB’s AI expertise since 2017 enables cutting-edge healthcare solutions:
• Strategic partnerships with research institutions like VNU’s Institute for AI
• Machine learning implementations for predictive analytics and clinical decision support
• Natural language processing for automated documentation and clinical insights
• Advanced analytics platforms supporting population health management and quality improvement
Cost Efficiency and Global Reach
HBLAB provides competitive advantages for healthcare organizations:
• 30% lower costs compared to native development markets without compromising quality
• Strong English proficiency ensuring clear communication and collaboration
• Global presence with experience serving clients across multiple healthcare markets
• Proven track record of successful healthcare software implementations and ongoing support
Comprehensive Healthcare Solutions
HBLAB’s healthcare portfolio encompasses the full spectrum of digital health technologies:
EMR/EHR Development
• Custom electronic medical record systems
• Legacy system modernization
• Cloud-based healthcare platforms
• Mobile health applications
Integration and Interoperability
• HL7 FHIR implementation
• API development and management
• Third-party system integrations
• Data migration and synchronization
Advanced Healthcare Technologies
• Telemedicine platforms
• Patient engagement portals
• Clinical decision support systems
• Population health management tools
Conclusion
Electronic Medical Record (EMR) systems have become indispensable for modern healthcare organizations, transforming patient care delivery and operational efficiency worldwide. With the global EMR market projected to reach $56 billion by 2033 and adoption rates exceeding 90% among US healthcare providers, EMR technology represents a fundamental shift in healthcare information management.
The compelling benefits of EMR implementation include substantial cost savings of $731 per patient admission, net ROI of $86,400 per provider over five years, and significant improvements in patient safety through 17.5% reduction in medical errors. These systems enhance care coordination, streamline clinical workflows, and provide real-time access to comprehensive patient information, ultimately improving healthcare outcomes and operational efficiency.
However, successful EMR implementation requires careful planning to address challenges including system integration complexity, user adoption barriers, and substantial upfront investments averaging $44,000 per provider. Organizations must prioritize comprehensive training, robust technical infrastructure, and ongoing support to maximize EMR benefits and ensure meaningful use.
As healthcare continues evolving toward digital transformation, EMR systems integrated with AI, interoperability standards, and emerging technologies will play increasingly critical roles in patient-centered care delivery. Healthcare organizations partnering with experienced technology providers like HBLAB can leverage specialized expertise, cost-effective development models, and proven implementation methodologies to achieve successful EMR adoption and long-term healthcare innovation.
The future of healthcare depends on intelligent, interoperable EMR systems that seamlessly connect providers, patients, and health information across the care continuum, making quality healthcare more accessible, efficient, and effective for populations worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between EMR and EHR systems?
EMR (Electronic Medical Record) systems are digital versions of patient charts used within a single healthcare organization, focusing on clinical documentation and internal workflows. EHR (Electronic Health Record) systems are more comprehensive platforms designed for data sharing across multiple healthcare providers and organizations, emphasizing interoperability and patient-centered care coordination.
2. How much does EMR implementation cost?
EMR implementation costs average $44,000 per provider for initial setup, with ongoing annual expenses of approximately $8,500 per provider. However, healthcare organizations typically achieve break-even within 10 months and realize net benefits of $86,400 per provider over five years through improved efficiency and cost savings.
3. What are the main benefits of EMR systems?
EMR systems provide significant advantages including 9.66% cost savings per patient admission, 17.5% reduction in medical errors, improved care coordination, enhanced patient safety through automated alerts, streamlined administrative processes, and better regulatory compliance. These systems also support evidence-based decision-making and population health management.
4. What challenges do healthcare organizations face during EMR implementation?
Common EMR implementation challenges include system slowness affecting 45.5% of providers, user resistance from 36.2% citing unfamiliarity, inadequate training impacting 38% of implementations, integration difficulties with legacy systems, and concerns about reduced patient interaction during consultations.
Which EMR vendors have the largest market share?Epic Systems dominates the EMR market with 37.7% share in acute care hospitals, followed by Oracle Health (Cerner) at 21.7%, Meditech at 13.2%, and Evident (CPSI) at 9%. Epic has shown the strongest growth, gaining 74 hospitals in 2024 while Oracle Health lost market share following acquisition challenges.
5. How do EMR systems improve patient safety?
EMR systems enhance patient safety through automated drug interaction warnings, allergy alerts, clinical decision support tools, standardized documentation processes, improved medication management, real-time access to patient information, and comprehensive audit trails. These features collectively reduce medical errors by 17.5% and improve overall care quality.
6. What role does AI play in modern EMR systems?
Artificial intelligence transforms EMR capabilities through predictive analytics for early disease detection, automated clinical documentation, pattern recognition in diagnostic data, population health insights, and intelligent decision support. Leading health systems report 100% adoption of AI-powered ambient documentation technologies, significantly improving provider efficiency and reducing burnout.
7. When should healthcare organizations implement EMR systems?
Organizations should prioritize EMR implementation when experiencing scalability challenges, regulatory compliance requirements, quality and safety concerns, competitive pressures for digital services, or when adequate funding and technical infrastructure are available. The decision should align with strategic goals and operational readiness.
8. How can healthcare organizations ensure successful EMR adoption?
Successful EMR adoption requires comprehensive planning including stakeholder engagement, adequate training programs, robust technical infrastructure, change management strategies, ongoing support resources, and partnership with experienced technology providers who understand healthcare workflows and regulatory requirements.
9. What is the ROI timeline for EMR systems?
EMR systems typically achieve positive ROI within 10 months of implementation, with healthcare organizations realizing net benefits of $86,400 per provider over five years. Cost savings come from reduced administrative expenses, improved billing accuracy, decreased medical errors, and enhanced operational efficiency.
Read More:
– Healthcare Software Development: 7 Powerful Trends Reshaping Global Care
– Will AI Replace Doctors? 6 Proven Facts and Limits
– Healthcare App Development: Revolutionizing Patient Care and Medical Practices




