In today’s competitive business landscape, delivering high-quality products and services is paramount. To achieve this, organizations rely on two critical quality management processes: Quality Control (QC) and Quality Assurance (QA). However, these terms are often used interchangeably, they present distinct differences, yet interconnected functions.
What are the Quality Assurance and Quality Control
First, we need to understand what the concepts of Quality Assurance and Quality Control are.
Quality Assurance (QA)
Quality Assurance (QA) is a systematic approach to ensuring that a product or service meets predefined quality standards. It’s a proactive process that involves planning, implementation, and control of quality-related activities to provide confidence that requirements will be fulfilled. In essence, QA is about preventing defects rather than detecting them.

Quality Control (QC)
Quality Control is a reactive process that focuses on identifying and eliminating defects in a finished product or service. QC involves inspecting products or services against predetermined standards.
While QA and QC are separate functions, they are interdependent. QA provides the framework for QC activities to be effective. A strong QA system can help prevent defects, reducing the workload for QC. On the other hand, QC data can provide valuable input for QA improvement initiatives.
5 Major Differences between Quality Assurance and Quality Control
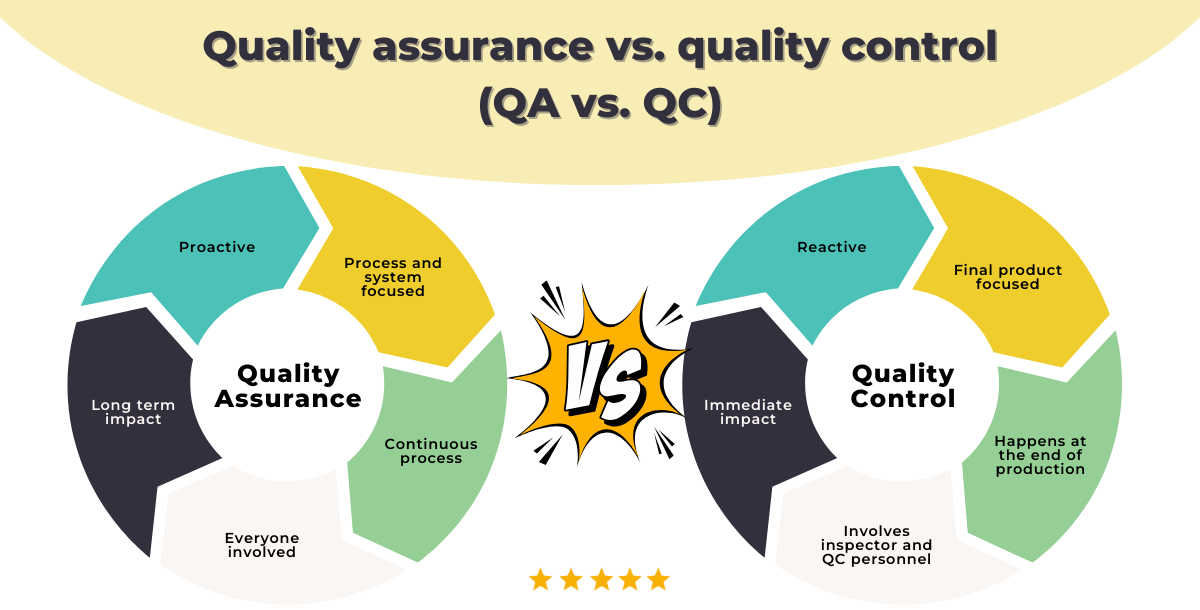
Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) are often misunderstood as interchangeable terms. While they both contribute to overall product or service quality, they have distinct roles and responsibilities. Let’s delve into the five primary differences between these two crucial functions.
| Criteria | Quality Assurance | Quality Control |
| Proactive vs. Reactive Approach | Proactive: Focuses on preventing defects before they occur. | Reactive: Focuses on identifying and fixing defects after they occur |
| Scope of Responsibilities | Covers the entire process, from planning to execution, ensuring that quality standards are integrated throughout. | Specific to the final product, checking that the outcomes meet the predefined quality standards. |
| Focus Area | Process-oriented: Ensures the processes used to create the product are adequate to meet quality standards. | Product-oriented: Ensures that the final product meets quality specifications and is free of defects. |
| Tools and Techniques | Process checklists, process audits, quality planning, training, and preventive actions. | Inspections, testing, reviews, statistical quality control (SQC), and defect tracking. |
| Role in the Organization | Part of management or the project team, focusing on improving and optimizing processes. | Part of the production team or a specialized quality department, focusing on product output |
1. Proactive & Reactive Approach
- Quality Assurance (QA): Embrace a proactive stance. It focuses on preventing defects before they occur by establishing and maintaining quality standards, processes and systems. QA is about creating a quality culture within an organization.
- Quality Control (QC): Takes a reactive approach. QC involves inspecting and testing products or services to identify defects after they have been produced. It’s about detecting and correcting quality issues.
2. Scope of Responsibility
- Quality Assurance (QA): Encompasses the entire product or service lifecycle, from design and development to production and delivery. QA is concerned with the overall quality system and its effectiveness.
- Quality Control (QC): Primarily focuses on the finished product or service. QC activities are centered around inspecting and testing to ensure compliance with specifications.
3. Focus Area
- Quality Assurance (QA): Concentrates on processes, systems, and procedures. QA aims to improve the overall quality of the process to prevent defects from happening in the first place.
- Quality Control (QC): Concentrates on the product or service itself. QC focuses on identifying defects in the final product or service.

4. Tools and Techniques
- Quality Assurance (QA): Employs tools and techniques like process mapping, quality audits, statistical process control (SPC), and quality management systems (QMS) to assess and improve processes.
- Quality Control (QC): Relies on tools and techniques such as inspection, testing, measurement, and calibration to evaluate product or service quality.
5. Role in the Organization
- Quality Assurance (QA): Often involves cross-functional teams and is integrated into the overall organizational structure. QA is responsible for developing and implementing quality policies and procedures.
- Quality Control (QC): Typically involves a dedicated QC team or individuals responsible for inspecting and testing products or services. QC is more focused on the production or service delivery phase.
The Relationship between QC and QA
While QA and QC are often discussed separately, they are intrinsically linked and form the backbone of any effective quality management system.
The Synergistic Relationship:
- QA sets the stage: Quality Assurance establishes the framework for quality. It involves planning, implementing, and controlling quality-related activities to ensure requirements are fulfilled. QA focuses on preventing defects by establishing processes and standards.
- QC verifies the outcome: Quality Control is the operational technique used to fulfill quality requirements. It involves inspecting and testing products to identify defects. QC is the final checkpoint before a product or service is released.
A Symbiotic Cycle:
The relationship between QA and QC can be visualized as a cycle:
- QA Planning: Establishing quality standards, processes and procedures
- QA Implementation: Implementing the defined quality system
- QC Inspection: Testing and inspecting products or services against standards.
- QC Feedback: Providing information on defects and process issues.
- QA Improvement: Using QC data to refine processes and standards.
Benefits of Implementing QC and QA
Implementing robust Quality Control (QC) and Quality Assurance (QA) practices can significantly enhance an organization’s performance and reputation. By working in tandem, these two functions contribute to a multitude of benefits.
Improved Product or Service Quality
- Reduced defects: QA’s proactive approach to process improvement helps prevent defects from occurring, while QC’s inspection process identifies and removes defective products.
- Enhanced customer satisfaction: Delivering consistently high-quality products or services leads to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Increased market share: A reputation for quality can give a business a competitive edge.
Cost Reduction
- Reduced rework: By identifying and preventing defects early in the process, QC and QA can significantly reduce the need for costly rework.
- Lower scrap rates: Improved quality leads to less waste and reduced material costs.
- Decreased warranty claims: Fewer product failures mean lower warranty costs.
Increased Efficiency
- Optimized processes: QA’s focus on process improvement can streamline operations, leading to increased efficiency.
- Faster time-to-market: Efficient processes and fewer defects can accelerate product or service delivery.
- Improved resource utilization: Effective QC and QA help ensure that resources are used optimally.

Enhanced Risk Management
- Mitigated risks: By identifying potential quality issues early, QA and QC can help mitigate risks associated with product failures or customer dissatisfaction.
- Improved regulatory compliance: Adherence to quality standards can help organizations meet regulatory requirements.
- Enhanced brand reputation: A strong commitment to quality can protect a company’s reputation in case of product recalls or other quality-related issues.
Improved Employee Morale
- Empowerment: Employees involved in QC and QA often feel empowered to contribute to the organization’s success.
- Reduced stress: A well-functioning quality system can reduce stress for employees by minimizing errors and rework.
- Increased job satisfaction: Employees who work in a quality-focused environment often experience higher job satisfaction.
By investing in QC and QA, organizations can reap significant benefits in terms of product quality, customer satisfaction, cost reduction, efficiency, risk management, and employee morale. These benefits contribute to overall business success and sustainability.
How to choose the right career path: Quality Assurance vs. Quality Control
Your Personality and Interests:
- Analytical and detail-oriented: If you enjoy problem-solving, analyzing data, and focusing on the nitty-gritty details of a product, QC might be a good fit.
- Strategic and process-oriented: If you prefer a broader perspective and enjoy planning, implementing, and improving processes, QA might be more appealing.
- People-oriented: Both QA and QC involve teamwork, but QA often requires stronger interpersonal skills for collaborating with cross-functional teams.
Skill Set:
- Technical skills: Both roles require technical knowledge, but QC often demands more hands-on experience with testing equipment and tools.
- Analytical skills: Both QA and QC require strong analytical skills, but QA places a greater emphasis on data analysis and process improvement.
- Communication skills: Effective communication is essential for both roles, but QA often involves more interaction with different departments and stakeholders.
Career Goals:
- Advancement: Both QA and QC offer opportunities for career growth, but QA often leads to management or leadership positions due to its broader scope.
- Industry focus: Consider the specific industry you’re interested in. Some industries may have a stronger emphasis on QA or QC.
- Work-life balance: Both roles can be demanding, but the nature of the work can vary. QC roles may involve more shift work or overtime, while QA roles might have more regular work hours.
Educational Background:
- Education requirements: Both QA and QC typically require a bachelor’s degree in engineering, science, or a related field. However, specific certifications may be beneficial.
- Continuous learning: Both fields require ongoing learning to stay updated with industry trends and technologies.
How to become a Quality Assurance or Quality Control
To become a Quality Assurance (QA) or Quality Control (QC) professional, you can follow a structured pathway that combines education, skill development, and practical experience. Here’s a detailed roadmap:
1. Educational Background
- High School Diploma or Equivalent: While not mandatory for all positions, having a strong foundation in mathematics and science will be beneficial.
- Bachelor’s Degree:
– Pursue a degree in fields related to quality, such as Engineering, Quality Management, Manufacturing, Business Administration, or a relevant scientific field.
– Coursework should include topics like statistics, quality control methods, process improvement, and project management.
- Advanced Degrees (Optional): Some positions may require or prefer candidates with a master’s degree in Quality Assurance, Engineering Management, or a related field.
2. Certifications
Certifications can significantly enhance your employability and demonstrate your commitment to quality practices. Consider the following:
- Certified Quality Engineer (CQE): Offered by the American Society for Quality (ASQ), this certification focuses on the principles of quality engineering.
- Certified Quality Auditor (CQA): Also from ASQ, this certification is ideal for those interested in auditing processes and systems.
- Six Sigma Certification: Learning Six Sigma methodologies can provide you with tools to improve processes and reduce defects. Levels range from Yellow Belt (beginner) to Black Belt (advanced).
- ISO Certifications: Familiarizing yourself with ISO standards relevant to your industry (e.g., ISO 9001) can be a valuable asset.
3. Developing Relevant Skills
- Technical Skills:
– Gain proficiency in quality management systems and tools used for data analysis, such as Minitab, Microsoft Excel, or statistical software.
– Understand quality control tools like control charts, Pareto charts, fishbone diagrams, and root cause analysis techniques.
- Analytical Skills:
Develop strong analytical skills to interpret data, identify trends, and diagnose issues effectively. Problem-solving skills are critical for determining root causes of defects.
- Communication Skills:
Effective communication is essential, as you’ll need to report findings, collaborate with cross-functional teams, and convey quality standards clearly.
- Attention to Detail:
Cultivate a meticulous approach to reviewing processes, documentation, and products to catch defects and ensure compliance with quality standards.
4. Gaining Experience
Here is a common roadmap to gain experience in becoming a Quality Assurance or Quality Control professional.
- Internships: Look for internships in QA/QC departments during your studies. This hands-on experience is invaluable for applying theoretical knowledge in practical situations.
- Entry-Level Positions: Seek entry-level roles such as Quality Inspector, Quality Technician, or QA Tester. These positions will provide exposure to quality processes and allow you to learn from experienced professionals.
- On-the-Job Training:Engage in on-the-job training opportunities offered by employers to enhance your skills in quality processes, testing methodologies, and documentation practices.
5. Networking and Professional Development
- Join Professional Organizations: Become a member of organizations such as ASQ or local quality control associations. Membership often provides access to resources, events, and networking opportunities.
- Attend Workshops and Conferences: Participate in industry workshops, seminars, and conferences to gain insights into the latest trends, tools, and best practices in QA/QC.
6. Continuous Learning
- Stay Updated: Regularly update your knowledge by taking additional courses on new quality methodologies, technologies, and industry standards.
- Pursue Additional Certifications: As you progress in your career, consider obtaining more advanced certifications or specialized training relevant to your field.
7. Advancing Your Career
- Seek Advanced Roles: With experience, you can pursue roles such as Quality Manager, QA/QC Lead, or Quality Director. These positions often involve leading quality initiatives, managing teams, and developing quality strategies.
- Develop Leadership Skills: Work on enhancing your leadership and management skills, as these will be essential for guiding teams and driving quality improvements.
- Specialization: Consider specializing in areas such as software quality assurance, manufacturing quality control, or regulatory compliance, depending on your interests and industry trends.
8. Industry-Specific Knowledge
Understand Regulatory Standards: Depending on your industry, familiarize yourself with specific quality standards and regulatory requirements (e.g., FDA regulations for pharmaceuticals, ISO standards for manufacturing).
Skills and Requirements for Quality Assurance and Quality Control Jobs
Quality Assurance (QA) jobs play a crucial role in maintaining and improving the quality of products and services. To succeed in this field, you need a combination of hard and soft skills. Below are some essential skills and requirements:
- Analytical Skills
QA professionals must possess strong analytical skills to identify potential problems in processes. They should be adept at analyzing data to improve processes and ensure compliance with quality standards.
- Attention to Detail
Precision is paramount in QA. Professionals in this field must pay close attention to detail to ensure that every aspect of a process meets established standards
- Process Improvement
Understanding methodologies such as Six Sigma, Lean, or Total Quality Management (TQM) can significantly enhance a QA professional’s ability to improve processes and eliminate waste.
- Project Management Skills
QA roles often involve managing multiple projects simultaneously. Strong project management skills help ensure the timely delivery of quality assurance activities.
- Communication Skills
QA professionals need to communicate effectively with various stakeholders, including developers, product managers, and customers. Clear communication helps in articulating quality standards and expectations.
Quality Control position requires skills like:
- Technical Skills
QC professionals need strong technical skills, especially if they are involved in testing software or products. Familiarity with testing tools and techniques is essential.
- Problem-Solving Skills
QC requires quick thinking and problem-solving abilities to identify defects and determine their causes. This skill is crucial for implementing corrective actions.
- Knowledge of Quality Standards
QC professionals should be well-versed in quality standards such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific regulations. This knowledge ensures that products meet the required specifications.
- Testing and Inspection Techniques
Proficiency in various testing methods (e.g., unit testing, integration testing) and inspection techniques is vital for QC roles. Familiarity with statistical process control (SPC) can also be beneficial.
- Attention to Detail
Just like in QA, attention to detail is critical in QC. Inspectors must be meticulous to ensure that products meet quality requirements.
What are the benefits of pursuing a career in quality management?
Pursuing a career in quality management can be a rewarding choice for several reasons. Here’s a detailed look at why this field might be the right path for you:
1. High Demand for Quality Professionals
As industries focus more on maintaining high standards and compliance, the demand for quality management professionals continues to grow. This trend ensures job security and numerous opportunities across various sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare, software development, and more.
2. Impact on Business Success
Quality management is crucial for the success of any organization. By implementing effective quality assurance and control processes, professionals can help improve product quality, reduce waste, enhance customer satisfaction, and ultimately contribute to the organization’s profitability.
3. Diverse Career Opportunities
A career in quality management offers a wide range of roles, such as Quality Assurance (QA) specialists, Quality Control (QC) inspectors, quality auditors, and quality managers. This diversity allows individuals to find a niche that aligns with their interests and strengths.
4. Skill Development
Working in quality management equips you with a valuable skill set that includes analytical thinking, problem-solving, project management, and effective communication. These skills are not only applicable to quality roles but also transferable across different fields, enhancing your overall employability.
5. Continuous Learning and Growth
The field of quality management is dynamic and ever-evolving, with new technologies, methodologies, and standards emerging regularly. This environment provides opportunities for continuous learning and professional development, keeping your career engaging and fulfilling.
6. Contribution to Customer Satisfaction
Quality management professionals play a vital role in ensuring that products and services meet or exceed customer expectations. By focusing on quality, these professionals enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty, which are essential for long-term business success.
7. Cross-Industry Applicability
The skills and knowledge gained in quality management are relevant across various industries, allowing for career flexibility. This versatility means that you can work in different sectors, broadening your experience and opportunities.
8. Leadership Opportunities
Many quality management roles involve leading teams and projects and providing opportunities to develop leadership skills. As you advance in your career, you may take on more significant leadership positions, which can be both fulfilling and rewarding.
9. Recognition and Credibility
Achieving certifications such as Certified Quality Auditor (CQA) or Certified Quality Engineer (CQE) can enhance your professional credibility. Being recognized as a quality management expert can open doors to advanced career opportunities and increase your value in the job market.
10. Contribution to Innovation
Quality management fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation. Professionals in this field have the opportunity to contribute ideas that can lead to the development of new products, services, or processes, making a meaningful impact on their organizations.
A career in quality management offers a blend of job security, skill development, and the opportunity to make a significant impact within organizations. If you have a passion for quality, problem-solving, and continuous improvement, this field can provide a fulfilling and rewarding career path. With the right skills and dedication, you can become an integral part of an organization’s success, ensuring that quality remains a top priority.
Conclusion
To achieve the highest level of quality in manufacturing, a synergistic approach combining Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) is essential. While QC focuses on identifying and rectifying defects in finished products, QA proactively establishes preventative measures throughout the entire production process. This dual strategy ensures consistent delivery of high-quality products by building a robust framework that minimizes errors and maximizes efficiency. By investing in both QA and QC, manufacturers demonstrate a commitment to excellence and customer satisfaction, ultimately leading to a competitive advantage in the market.
See more:
– No-Code Test Automation: The Ultimate Success Blueprint
– Data-Driven Business Strategy: The Key to Unleashing Breakthrough Growth
– Automatic Data Processing: The Complete Guide to Transforming Business Operations




