Discover how healthcare software development, custom solutions, and advanced services empower the global healthcare industry. Explore the evolution, operations, benefits, challenges, and expert insights for IT leaders in this industry of Healthcare Software Development.
Introduction: The Global Rise of Healthcare Software Development
Did you know that over 68% of healthcare providers worldwide have adopted new digital platforms to boost patient care and operational efficiency? In today’s fast-evolving healthcare sector, healthcare software development is no longer just an option—it is the backbone of innovation, compliance, and patient-centered care. Whether you represent a hospital, clinic, health startup, or enterprise group, the adoption of leading-edge healthcare software is critical for staying ahead in the global race for healthcare excellence.
What is Healthcare Software Development?

Healthcare software development refers to the design, building, testing, and deployment of specialized software systems for the healthcare industry. These solutions range from Electronic Health Records (EHR) platforms to telemedicine apps, patient engagement tools, medical billing software, and compliance systems.
Custom healthcare software development allows organizations to tailor every aspect of their solutions, ensuring compatibility with unique clinical workflows, regulatory requirements (like HIPAA, GDPR), and integration with third-party systems. As the healthcare software development industry continues to grow, solutions are increasingly focused on interoperability, user experience, and security.
Common use cases include:
- Electronic Medical Record (EMR) systems with real-time data sync
- Telehealth and virtual care platforms
- Hospital management software
- AI-powered decision-support tools
The Digital Evolution of Healthcare: Why Healthcare Software Development Took Off
Early Hopes and Roadblocks
In the 1960s, people began thinking about how computers could help doctors. The hope was that computers would make it faster to get lab results, help doctors keep up with research, and reduce mistakes thanks to digital alerts. But early computers were expensive, slow, and not reliable. Most doctors and hospitals didn’t see the value, and equipment costs were just too high to justify widespread use.
Laying the Groundwork

Things started changing in the 1980s. Personal computers and networks showed up in hospitals, making sharing information a bit easier. The healthcare industry realized that systems needed to “talk” to each other. This need led to the creation of standards like HL7 for safely exchanging data between different health systems. Still, many organizations hesitated because money was tight, and new systems were seen as expensive experiments.
Alongside this, digital images became possible. CT scans and digital X-rays started replacing film, but storing and sharing these images was tricky at first. Developers began building picture archiving and communication systems (PACS), which allowed doctors to access scans from more than one location.
The Push for Better Records
In the 1990s, expert groups called for digital records that focused on helping patients — not just tech for the sake of it. Electronic medical records (EMRs) promised dynamic, safe access to patient history. But costs and privacy fears limited adoption. The U.S. passed HIPAA in 1996, demanding greater security for digital health records, which set new expectations for the industry.
The internet also changed things. It let doctors, patients, and researchers connect in ways that were never possible before. Suddenly, sharing and searching for health information became possible on a global scale.
Demand Heats Up
As computers got better, hospitals and researchers could see patterns in how care varied across locations and providers. They could spot where mistakes were made and what worked best. Reports from major health leaders made it clear: if healthcare didn’t modernize, it risked falling behind.
By the early 2000s, health and tech policies required better standards. EMRs needed to be certified, data had to be interoperable, and hospitals were encouraged (or even rewarded) for going digital.
The Data Boom
Healthcare quickly became one of the most data-rich industries in the world. By 2020, the amount of health data created would reach nearly 2,300 exabytes—a mind-boggling number growing by about 50% per year. Data poured in from tests, scans, devices, and different departments—often all for a single patient.
Modern healthcare software helps make sense of all this complexity. Today’s systems organize, connect, and analyze everything from lab results and images to genetic and wearable data. Instead of isolated records, care teams have full, up-to-date patient snapshots in seconds.
Enter the Age of Smart Healthcare
The latest wave is artificial intelligence and automation. Smart software now assists with diagnosis, highlights potential issues, and helps coordinate care. Standards for data, privacy, and user IDs ensure that information is both useful and safe across all connected systems.
Why Did Demand Surge?
The push for healthcare software development happened because:
- Data became too huge and complex for paper or old systems.
- Patients and providers wanted more personalized, safer care.
- Regulators and insurers demanded better tracking and transparency.
- Global collaboration in research and care required shared standards.
- Crises like COVID-19 sped up digital adoption—telemedicine, mobile apps, remote monitoring, and more.
How Does Healthcare Software Development Work?
The process of software development in healthcare is rigorous and multi-phased, ensuring both innovation and compliance at every stage. Here’s a typical workflow:
- Discovery & Requirement Analysis: Understanding the unique challenges, compliance needs, and operational bottlenecks of the client.
- Strategic Planning: Defining the technology stack, project goals, and key milestones.
- Design & Prototyping: Creating user-friendly UX/UI with direct input from clinical/end-user stakeholders.
- Development: Building core features, ensuring secure architectures, focusing on scalability and interoperability in healthcare.
- Integration & Testing: Seamless integration with existing hospital, insurance, or third-party systems. Comprehensive testing for security, compliance, and usability.
- Deployment & Support: Fast rollout, with ongoing support and continuous improvement.
A focus on custom healthcare software development allows for bespoke features like smart scheduling, advanced analytics, and automated compliance checks—often not available in off-the-shelf products.
Key Benefits of Healthcare Software Development
Modern healthcare software development services drive operational excellence and clinical innovation. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced Patient Outcomes: Faster decision-making and improved care coordination.
- Cost and Resource Efficiency: Automated billing, reduced paperwork, and better resource utilization.
- Regulatory Compliance: Built-in HIPAA/GDPR support and audit trails.
- Seamless Integration: Compatibility with diverse data sources—critical in the software development healthcare industry.
- Actionable Insights: Advanced analytics and reporting for continuous quality improvement.
👉 From ideation to ongoing support, HBLAB delivers end-to-end healthcare software development services to global healthcare leaders.
Challenges and Risks in Healthcare Software Development
Despite its promise, healthcare software development faces unique challenges:
- Data Security & Privacy: Threats of data breaches can lead to severe regulatory and reputational damage. Choosing the right healthcare software development services is critical for robust encryption, secure authentication, and regular compliance audits.
- Complex Integration: Legacy systems may not “talk” to new digital tools—causing workflow friction.
- User Adoption: Clinician and staff resistance to change can jeopardize even the best-designed solutions.
- Cost Overruns & Delays: Inadequate planning or unskilled vendors often drive up budgets.
🔎 Mitigation strategies include pilot deployments, robust user training, regular updates, and choosing vendors with proven healthcare domain experience.
Custom Healthcare Software Development: Approaches and Use Cases
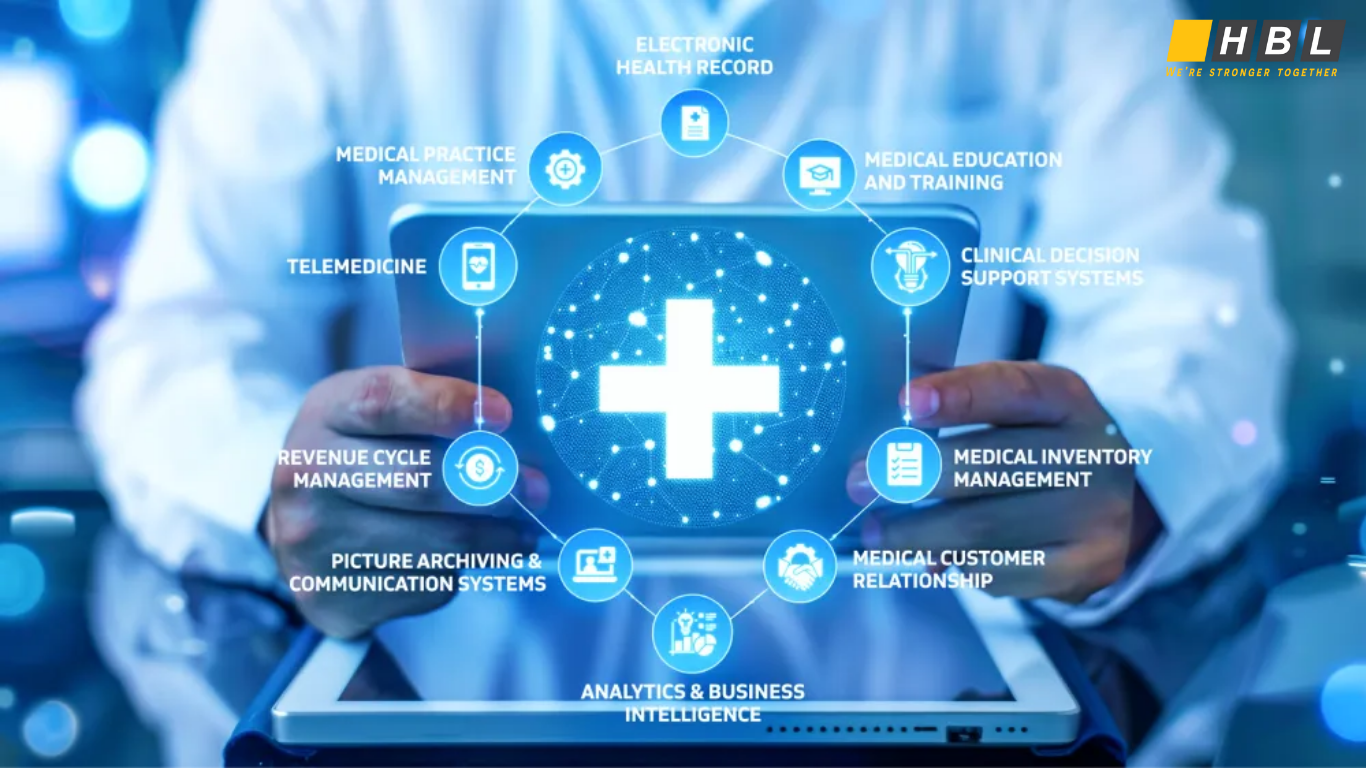

When should organizations opt for custom healthcare software development over off-the-shelf solutions?
- Specialized Workflows: Hospitals with unique care coordination, reporting, or compliance needs.
- Security-First Environments: Research labs requiring next-level data privacy.
- Rapid Scaling: Health systems expanding to new locations and needing uniform data standards.
- Integration Demands: Sites integrating IoT medical devices, or remote monitoring networks.
Emerging Trends Redefining Healthcare Software Development in 2026
Digital transformation is fundamentally altering healthcare and software is at the heart of almost every breakthrough.
1. Telehealth & Virtual Care: The “New Normal” in Healthcare Delivery
Telehealth has rapidly evolved from a crisis response to a core pillar of care. No longer a temporary solution, virtual health platforms now extend medical services far beyond the hospital’s four walls — supporting video visits, remote consultations, and even hospital-at-home programs.
In fact, roughly 25% of Medicare services in the U.S. could shift to home care by 2026. This shift is driven by patient preference and convenience: over half of U.S. patients say they’re more satisfied with care thanks to telehealth (Statista). For healthcare leaders, virtual and hybrid care models are no longer “nice to have” — they’re essential for long-term strategy (Deloitte). But making this seamless for users demands deep integration with EHRs, scheduling, and billing tools.
2. Wearables & Remote Monitoring: Real-Time Data, Real-World Care
Wearable health tech has exploded in adoption. From smartwatches to biosensor patches, these tools are giving both patients and clinicians access to real-time data — well beyond the walls of the clinic.
Globally, more than one billion wearable devices are expected to be in use by 2026. These devices power remote patient monitoring programs, enabling early intervention for chronic conditions and post-surgical recovery. Notably, 88% of doctors want patients to track key health stats at home, and the wearables market is set to triple in value by 2029.
Success, however, hinges on more than just collecting data — robust accuracy, mature interoperability, and privacy by design are all mandatory as digital health expands.
3. AI & Machine Learning: Smarter Diagnostics, Predictive Care

AI in healthcare is no longer on the horizon — it’s here and accelerating. Nearly 9 out of 10 healthcare organizations are using AI in some form (HIMSS). The most popular use is in diagnostics: over two-thirds of FDA-cleared AI medical devices focus on medical imaging, helping radiologists spot subtle patterns in scans earlier and with higher accuracy.
AI isn’t only about clinical insights. Hospitals are leveraging machine learning to automate compliance, forecast patient needs, and improve operations. But as algorithms take on bigger roles, ensuring transparency, fairness, and regulatory compliance has become paramount — especially as new laws like the EU AI Act gain traction.
4. Generative AI & Intelligent Workflow Automation
Generative AI — think large language models like GPT — is shaking up healthcare operations. More than 40% of healthcare executives are already seeing ROI from generative AI tools (Deloitte). Their biggest impact? Cutting out administrative headaches by:
- Summarizing patient histories in seconds
- Auto-generating clinical notes
- Translating medical terms into everyday language
Patients benefit as well, with AI-powered chatbots providing immediate answers and support for chronic conditions. As clinicians confront burnout, reducing paperwork with reliable AI support frees up time for actual care.
Of course, generative AI in healthcare brings real challenges — bias, accuracy, and privacy concerns are at the forefront. Successful deployment demands strong governance and human oversights.
👉 Contact HBLAB today to transform your healthcare journey!
5. Interoperability & EHR Modernization: Breaking Down Data Silos
For all the talk of digital health, much patient data is still locked in disconnected systems. That’s changing fast. Interoperability has become a strategic priority, empowering seamless, secure data flow between hospitals, clinics, devices, and patients’ own wearables.
Recent regulations and growing investment into cloud-native EHRs (Electronic Health Records) are accelerating integration. 60% of healthcare leaders are investing more in core platforms not only to upgrade but to connect and streamline systems across the care continuum (Deloitte). Data interoperability means more holistic and personalized care — whether syncing remote-monitoring data, updating treatment plans, or matching claims with treatments.
6. Personalized & Precision Care Platforms
Healthcare is swiftly moving from “one size fits all” to truly individualized medicine. Enabled by AI, genomics, and huge data sets, platforms can now tailor interventions based on a person’s biology, digital health records, and even daily behaviors.
Precision medicine is set to be a multi-billion-dollar market by 2032. In practice, this means more targeted therapies, predictive risk models, and even “digital twins” — dynamic, virtual versions of patients that help clinicians test different treatments before applying them in real life. The challenge for developers: seamless aggregation and analysis of diverse, sensitive data streams to enable precision care at scale.
7. Digital Mental Health Solutions: Care Beyond the Clinic
Mental health has jumped to the forefront of healthcare priorities, especially as virtual therapy proves its value. Digital platforms for mental health support — from teletherapy to AI-powered chatbots to tracking apps — are booming, with the global market expected to grow at over 14% CAGR and reach $17.5 billion by 2030.
These technologies are enabling hybrid care models, greater accessibility, and continuous support between traditional sessions. For organizations, integrating mental health solutions securely and empathetically is a must.
8. Cybersecurity & Data Privacy: The Non-Negotiable Foundation
With every advance in connected platforms comes greater risk. Healthcare is now a prime target for cyber attacks — ransomware, phishing, data breaches, and vulnerable IoT devices are rising threats.
In 2024 alone, there were 181 confirmed ransomware attacks on healthcare providers (HIPAA Journal), and the average cost of a health data breach hit $10.93 million — more than any other industry.
To meet this challenge, organizations are deploying zero-trust architectures, AI-driven threat detection, and rigorous user training. Privacy isn’t optional — it’s a differentiator. As patient data becomes more distributed and valuable, trust, safeguarded by world-class security, is the single most important foundation for any healthcare software.
When to Invest in Software Development for Healthcare?
You should prioritize healthcare software development when:
- Scaling operations to new locations or service lines
- Facing new compliance requirements or regulatory changes
- Needing deeper analytics, patient engagement, or AI-powered diagnostics
- Seeking differentiation in highly competitive markets
Customized solutions offer a decisive edge where generic software falls short—especially in complex, compliance-driven environments.
HBLAB: Your Trusted Partner in Healthcare Software Development

Why partner with HBLAB?
- 10+ years in custom healthcare software: Deep expertise from EHRs to AI-powered solutions
- 630+ IT professionals: 30% senior-level, experienced in global and complex projects
- CMMI Level 3 Certified: Commitment to quality, process, and information security
- Flexible engagement: Offshore, onsite, or dedicated teams—adapted to your specific needs
- Cost efficiency: World-class talent at up to 30% lower cost than native markets
- AI since 2017: Early adoption, strong research partnerships (e.g., VNU Institute for AI)
- Strong communication: multilingual teams, transparent delivery
CONTACT US FOR A FREE CONSULTATION
Read more:
– Medical Software Programs Breaking Barriers: 5 Unstoppable Forces Shaping Tomorrow’s Health
– Dominate 2026 with a Winning AI Strategy Consulting Blueprint
– IT Outsourcing Trends 2026: Market Dynamics and Emerging Technologies