70% of digital transformation initiatives fail to meet their objectives—yet organizations that succeed achieve 71% revenue growth and 62% better decision-making. What separates winners from the costly failures?
Quick Answer: What You Need to Know
A digital transformation company helps organizations integrate digital technologies across all business areas to improve operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive competitive advantage. These companies provide consulting, implementation, and support services spanning cloud migration, AI integration, process automation, and organizational change management.
Global digital transformation spending will reach $3.9 trillion by 2027, growing at 16.2% annually, as businesses recognize transformation as essential for survival. However, only 35% of companies achieve their digital transformation goals—success requires the right partner, clear strategy, proper change management, and sustained executive commitment.
What is a Digital Transformation Company?
A digital transformation company is a specialized service provider that guides organizations through the complex journey of integrating digital technology into every aspect of their business operations. Unlike traditional IT consultancies that focus narrowly on technology implementation, digital transformation companies take a holistic approach—addressing strategy, culture, processes, technology, and organizational change simultaneously.

These companies serve as strategic partners rather than mere vendors, helping businesses fundamentally rewire how they operate to build competitive advantages through continuous deployment of technology at scale.
The scope extends beyond digitization (converting analog to digital) or digitalization (improving existing processes with digital tools) to encompass complete business model transformation and cultural evolution.
Digital transformation companies typically provide:
- Strategic Consulting: Business model innovation, digital strategy development, technology roadmapping, and competitive positioning
- Technology Implementation: Cloud migration, AI/ML integration, IoT deployment, blockchain solutions, and enterprise system modernization
- Process Optimization: Workflow automation, supply chain digitalization, customer journey mapping, and operational excellence
- Change Management: Organizational readiness assessments, training programs, stakeholder engagement, and culture transformation
- Ongoing Support: Continuous improvement frameworks, performance monitoring, and adaptive optimization
The distinction between successful digital transformation companies and traditional consultancies lies in their ability to bridge the gap between technology and business outcomes. According to McKinsey research, 90% of organizations are currently undergoing some form of digital transformation, making the selection of the right partner more critical than ever.
Why Businesses Need Digital Transformation Companies
The imperative for digital transformation has shifted from competitive advantage to survival necessity. Global spending reached $2.5 trillion in 2024 and continues accelerating as organizations face mounting pressure from multiple fronts.
The Digital Survival Imperative
Customer expectations have fundamentally changed. Research shows that 57% of consumers consider innovation absolutely critical when choosing companies to purchase from, while 70% say new technologies have made it easier to take their business elsewhere.
This democratization of choice means businesses can no longer rely on legacy advantages—customers expect seamless digital experiences, 24/7 accessibility, and personalized engagement.
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated digital adoption timelines by years, forcing organizations to rapidly experiment with technologies they had previously sidelined. Remote work, contactless transactions, e-commerce, and digital customer service transformed from nice-to-have to mission-critical overnight.
Organizations that had invested in digital foundations before the crisis adapted quickly; those without struggled or failed.
Complex Technical and Organizational Challenges
Digital transformation presents multifaceted challenges that exceed internal capabilities for most organizations:
Technical Complexity: Integrating cloud architectures, AI/ML models, IoT sensors, and legacy systems requires specialized expertise. Organizations face decisions about build-vs-buy, cloud provider selection, security architecture, and scalability—decisions with multi-year consequences.
Talent Scarcity: Research indicates that 27% of organizations cite gaps in technical talent as a primary transformation obstacle, while 41% report skills gaps as critical impediments. The demand for data scientists, cloud architects, AI engineers, and DevOps specialists far exceeds supply.
Change Management Failures: Organizations with formal change management strategies are 7x more likely to achieve transformation goals. Yet 32% cite complexity of current environment and siloed mindsets as their biggest challenge. Technology alone doesn’t transform businesses—people do.
Financial Risk: Failed transformations cost organizations an average of 12% of annual revenue through wasted investment and opportunity costs. With such high stakes, organizations need partners who can de-risk initiatives through proven methodologies and experience.
Strategic Advantages of Partnering with Digital Transformation Companies
- Accelerated Time-to-Value: Transformation companies bring pre-built frameworks, proven methodologies, and reusable assets that compress implementation timelines. What might take internal teams 18-24 months can often be achieved in 6-12 months with expert guidance.
- Cross-Industry Insights: Leading transformation companies work across industries, identifying patterns and transferring best practices. They’ve seen what works, what fails, and why—insights that prevent costly mistakes.
- Objective Perspective: Internal teams often face political constraints, legacy thinking, and organizational blindspots. External partners provide unbiased assessments and can champion necessary but difficult changes.
- Flexible Scaling: Rather than hiring permanent staff for specialized skills needed temporarily, organizations can access expertise on-demand, scaling resources up during implementation and down during steady-state.
How Digital Transformation Companies Deliver Value
Successful digital transformation companies follow structured methodologies that balance quick wins with long-term strategic transformation. While specific frameworks vary, leading firms share common approaches rooted in business value realization.
Discovery and Assessment Phase
Transformation begins with comprehensive diagnostic work. Companies conduct digital maturity assessments evaluating current capabilities across technology infrastructure, data management, process efficiency, organizational culture, and customer experience.
This phase typically includes:
- Stakeholder interviews with C-suite executives, business unit leaders, IT teams, and frontline employees
- Technical architecture review examining existing systems, integration points, technical debt, and infrastructure constraints
- Process mapping documenting current workflows, identifying inefficiencies, and quantifying improvement opportunities
- Competitive benchmarking comparing digital capabilities against industry peers and best-in-class organizations
- Gap analysis determining the distance between current state and desired future state
The output is a prioritized transformation roadmap with sequenced initiatives, resource requirements, timeline projections, and expected business outcomes. Leading companies use value-effort matrices to identify quick wins that build momentum while laying groundwork for complex, high-value transformations.
Strategy Development and Road mapping
Digital transformation companies help organizations craft clear, actionable strategies aligned to business objectives. This involves defining specific domains (customer journeys, processes, or functional areas) to transform rather than pursuing scattered use cases.
Effective strategies include:
- Vision articulation: Clear statements of what the organization will become and why transformation matters
- Business case development: Financial modeling demonstrating ROI, payback periods, and value realization timelines
- Technology selection: Evaluating platforms, tools, and architectures that balance innovation with practical implementation
- Capability building plans: Identifying skills gaps and designing training, hiring, or partnering strategies
- Risk mitigation frameworks: Anticipating obstacles and designing contingency plans
McKinsey research emphasizes that successful transformations focus on complete domains rather than isolated use cases because this encompasses all related activities needed to deliver complete solutions.
For example, rather than just digitizing customer onboarding, transforming the entire customer acquisition and activation journey.
IN-DEPTH DOCUMENTS AND ROADMAPS FOR YOUR BUSINESS
Implementation and Integration
The implementation phase brings strategies to life through coordinated execution. Digital transformation companies typically establish cross-functional teams combining their specialists with client personnel, fostering knowledge transfer while maintaining momentum.
Key implementation activities:
- Cloud Migration: Moving workloads to cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) using lift-and-shift, refactoring, or cloud-native rebuilding approaches depending on application complexity and strategic importance.
- Data Platform Development: Building centralized data infrastructures that break down silos, establish governance, and enable analytics. This includes data lakes, warehouses, ETL pipelines, and master data management.
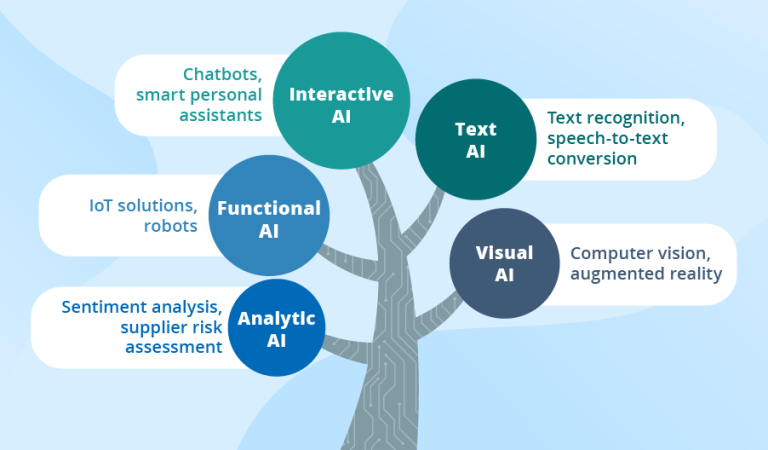
- AI/ML Integration: Deploying artificial intelligence for predictive analytics, intelligent automation, chatbots, recommendation engines, and decision support systems. Successful implementations start with high-value, well-defined use cases rather than experimental “AI for AI’s sake” projects.
The Foundational Knowledge for AI/ML Integration
- Process Automation: Implementing robotic process automation (RPA), intelligent document processing, and workflow orchestration to eliminate manual work and improve efficiency.
- API Development: Creating API layers that enable system integration, support omnichannel experiences, and facilitate ecosystem partnerships.
- Legacy Modernization: Updating or replacing outdated systems that constrain innovation. Approaches range from gradual refactoring using strangler fig patterns to complete replacement with modern platforms.
Throughout implementation, leading companies follow agile methodologies with 2-4 week sprints, continuous testing, and iterative refinement based on user feedback.
Change Management and Adoption
Technology implementation represents only half the transformation equation. Organizations investing one dollar in solution development should plan to spend at least another dollar on change management, training, and adoption initiatives.
Digital transformation companies facilitate organizational change through:
- Communication Programs: Multi-channel campaigns explaining the transformation vision, progress updates, and celebrating successes. Effective communication addresses “what’s in it for me” for different stakeholder groups.
- Training and Enablement: Designing role-based training programs, creating documentation and job aids, and establishing centers of excellence that support ongoing learning.
- Stakeholder Management: Identifying transformation champions, neutralizing resistors, and building coalitions of support across organizational levels.
- Adoption Monitoring: Tracking usage metrics, gathering feedback, and addressing barriers to adoption through iterative improvements.
Research consistently shows that cultural and organizational barriers exceed technology obstacles as causes of transformation failure. Companies that treat digital transformation as purely an IT initiative rather than an enterprise-wide business transformation are significantly more likely to fail.
Digital Maturity Assessment: Evaluating Your Organization’s Transformation Readiness
Before embarking on digital transformation, organizations must understand their current capabilities and readiness. This assessment framework helps you diagnose where you are and prioritize next steps.
The Five-Level Digital Maturity Model
Level 1 – Resistant (Traditional)
A digital transformation company sees organizations here operating mostly on analog processes with reactive tech adoption and siloed data, posing existential risk without immediate action.
-
Characteristics: Paper-based processes, disconnected systems, no data strategy, technology-averse culture.
-
Priority Actions: A digital transformation company will secure executive sponsorship, run a readiness assessment, and deliver 2–3 quick wins to build momentum.
Level 2 – Exploring (Opportunistic)
A digital transformation company typically finds isolated pilots and minimal integration, with leadership aware of the need but underinvested.
-
Characteristics: Some cloud adoption, departmental solutions, emerging data awareness, inconsistent skills.
-
Priority Actions: Partner with a digital transformation company to create a roadmap, establish governance, and pilot integration projects.
Level 3 – Repeatable (Formalized)
A digital transformation company helps formalize strategy, budgets, and methods as multiple projects prove value, though change hasn’t scaled organization-wide yet.
-
Characteristics: Cloud-first strategy, data governance, agile practices, growing cross-functional collaboration.
-
Priority Actions: Use a digital transformation company to scale winning patterns, upskill teams, and tie delivery to business outcomes.
Level 4 – Managed (Strategic)
A digital transformation company supports embedded capabilities, integrated systems, and proactive adoption of new tech with a culture of continuous improvement.
-
Characteristics: Enterprise digital ecosystem, advanced analytics, automation at scale, innovation culture.
-
Priority Actions: A digital transformation company can broker ecosystem partnerships, guide AI/IoT/blockchain pilots, and expand market reach.
Level 5 – Optimizing (Transformational)
A digital transformation company recognizes digital-native operations where strategy and technology are inseparable and innovation is continuous.
-
Characteristics: AI-driven operations, real-time adaptive systems, ecosystem orchestration, ongoing disruption.
-
Priority Actions: Work with a digital transformation company to codify best practices, incubate new models, and scale into new markets.
Get your free Digital Maturity Check
Assessment Dimensions
Evaluate your organization with or without a digital transformation company across five dimensions:
-
Technology Infrastructure: Cloud maturity, integration, APIs, automation, cybersecurity.
-
Data Capabilities: Governance, quality, analytics sophistication, AI/ML deployment, real-time processing.
-
Process Maturity: Automation depth, standardization, workflow optimization, journey mapping, agility.
-
People and Culture: Skills distribution, innovation mindset, change readiness, collaboration, leadership commitment.
-
Customer Experience: Omnichannel strength, personalization, self-service, digital engagement, feedback loops.
👉 Pro Tip: A digital transformation company will flag that maturity levels often vary by dimension—Level 4 in technology but Level 2 in culture is common. Focus first on the lowest-maturity bottlenecks to unlock transformation velocity.
Technical Architecture Blueprint for Scalable Digital Transformation
Digital transformation success depends on building technology foundations that are scalable, resilient, and adaptable. This technical blueprint provides guidance for enterprise architects and IT leaders.
Cloud-First Architecture Principles

Modern digital transformation assumes cloud as the default platform for new applications and workloads. The question isn’t whether to move to cloud but how to optimize the journey.
- Multi-Cloud vs. Single-Cloud Strategy: Organizations must decide between committing to a single cloud provider (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) or adopting multi-cloud approaches. Single-cloud strategies offer deeper integration and simplified management but create vendor lock-in. Multi-cloud provides resilience and negotiating leverage but increases complexity.
- Hybrid Cloud Integration: Most enterprises maintain hybrid architectures with some workloads remaining on-premises due to regulatory requirements, data sovereignty concerns, or technical constraints. Successful hybrid strategies require robust connectivity, consistent security policies, and unified management platforms.
- Cloud-Native Development: Building applications specifically for cloud environments using microservices, containers (Docker/Kubernetes), and serverless computing enables greater scalability and resilience than simply migrating legacy applications to cloud infrastructure.
- API-First Integration Architecture: Digital transformation requires connecting disparate systems, partners, and customers through well-designed APIs (Application Programming Interfaces).
- API Gateway Pattern: Implement centralized API gateways that handle authentication, rate limiting, protocol translation, and monitoring. This provides a consistent interface for consuming applications while abstracting backend complexity.
- Microservices Architecture: Decompose monolithic applications into smaller, independently deployable services that communicate via APIs. This enables teams to innovate on specific capabilities without impacting the entire system.
- Event-Driven Architecture: Implement publish-subscribe patterns where systems react to events rather than requiring synchronous communication. This reduces coupling and improves scalability for high-volume scenarios.
- Data Mesh Approach: Rather than centralizing all data in a single warehouse, distribute data ownership to domain teams while maintaining federated governance. This balances agility with control at enterprise scale.
- Real-Time Data Pipelines: Implement streaming architectures using technologies like Apache Kafka that enable real-time analytics rather than batch processing. This supports operational use cases requiring immediate insights.
- AI/ML Platform Infrastructure: Build reusable platforms that provide data scientists and developers with tools, compute resources, and deployment pipelines for machine learning models. This accelerates AI adoption beyond isolated experiments.
Security and Compliance Architecture
- Zero Trust Security Model: Abandon perimeter-based security in favor of continuous verification. Assume breach and verify every access request regardless of source location.
- Privacy by Design: Embed privacy controls and data protection into systems from inception rather than retrofitting compliance. This includes encryption, access controls, audit logging, and data minimization.
- DevSecOps Integration: Incorporate security testing and compliance checks into CI/CD pipelines so that security becomes an automated gate rather than a manual checkpoint.
Scalability and Resilience Patterns
- Auto-Scaling Infrastructure: Configure systems to automatically add or remove resources based on demand, optimizing cost while maintaining performance.
- Circuit Breaker Pattern: Implement failure isolation so that issues in one component don’t cascade throughout the system. Services detect failures and route around them.
- Multi-Region Deployment: Distribute applications across geographic regions to ensure availability even if an entire data center fails.
👉 Pro Tip: From our experience at HBLAB, organizations often underestimate the complexity of legacy system integration. Rather than pursuing complete replacement (which carries high risk), consider strangler fig patterns where new capabilities gradually replace old ones while maintaining business continuity.
Key Advantages of Partnering with Digital Transformation Companies
Organizations that successfully partner with digital transformation companies realize significant competitive advantages beyond what internal teams can achieve alone.
Access to Specialized Expertise Across Domains
Digital transformation requires diverse skill sets rarely found in single organizations. Transformation companies employ multidisciplinary teams spanning strategy consultants, enterprise architects, data scientists, UX designers, change management specialists, and industry experts.
This breadth enables them to address the full spectrum of transformation challenges. A financial services transformation might require cloud architects to design secure infrastructure, AI specialists to build fraud detection models, compliance experts to ensure regulatory adherence, and change managers to drive user adoption—all coordinated under a unified strategy.
Senior Talent Concentration: Leading transformation companies maintain high percentages of senior professionals with 10-15+ years of experience. This expertise accelerates problem-solving and reduces costly mistakes.
Accelerated Time-to-Value Through Proven Methodologies
Transformation companies bring battle-tested frameworks refined across hundreds of engagements. Rather than inventing approaches from scratch, they apply proven patterns adapted to your specific context.
- Reusable Assets and Accelerators: Pre-built reference architectures, code libraries, integration connectors, and automation scripts compress development timelines. What might take 6-8 months to build from scratch can often be deployed in 6-8 weeks using accelerators.
- Risk Mitigation: Having implemented similar transformations repeatedly, experienced companies anticipate obstacles before they materialize. They’ve developed solutions for common integration challenges, organizational resistance patterns, and technical bottlenecks.
Cost Efficiency and Flexible Resource Scaling
Lower Total Cost: Despite professional services fees, partnering with transformation companies often costs less than building internal capabilities. Organizations avoid recruitment costs, training investments, and the overhead of retaining specialized skills needed only periodically.
Research indicates that cost-efficient delivery models can reduce expenses by 30% or more compared to hiring equivalent talent in high-cost markets. Offshore and nearshore delivery centers provide access to skilled professionals at significantly lower rates.
Scalability: Transformation demands surge during implementation phases and decline during steady-state operations. External partners scale resources dynamically—ramping up teams quickly for urgent initiatives and scaling down afterward—providing flexibility that permanent headcount cannot match.
Transfer of Knowledge and Capability Building
Strategic partnerships emphasize knowledge transfer rather than creating dependencies. Transformation companies embed consultants alongside client teams, facilitating hands-on learning through collaboration.
Formal training programs, documentation, and centers of excellence ensure that internal teams can sustain and extend capabilities after external partners transition out. The goal is building self-sufficient organizations, not perpetual consulting engagements.
Objective Perspective and Change Catalyst
Internal teams often face political constraints, legacy assumptions, and organizational blindspots. External partners provide unbiased assessments and can champion necessary but unpopular changes without career risk.
They serve as change catalysts, helping executives build consensus, overcome resistance, and maintain momentum when transformation efforts face inevitable obstacles.
Common Challenges in Digital Transformation and How Companies Address Them
Even with expert partners, digital transformation presents significant challenges. Understanding these obstacles and mitigation strategies improves success probability.
Challenge 1: Complexity of Current Environment and Siloed Operations
The Problem: 32% of organizations cite complexity of current environment and siloed mindsets as their primary transformation challenge. Legacy systems built over decades create intricate dependencies that are poorly documented and difficult to untangle.
Different departments operate independent systems with inconsistent data, making enterprise-wide integration extremely difficult. Marketing uses one CRM, sales uses another, and customer service relies on separate ticketing systems—creating fragmented customer views.
How Companies Address It: Leading transformation companies begin with comprehensive discovery to map existing landscape—documenting systems, integrations, data flows, and dependencies. They employ strangler fig patterns that gradually replace legacy capabilities with modern alternatives while maintaining business continuity rather than risky “big bang” replacements.
API layers and integration platforms create abstractions that connect disparate systems without requiring complete replacement. Data integration tools synchronize information across silos, creating unified views even when underlying systems remain separate.
Challenge 2: Gaps in Technical Talent and Digital Skills
The Problem: 27% of senior leaders identify gaps in technical talent as major transformation impediments, while 41% cite skills gaps as critical challenges. The demand for cloud architects, data scientists, AI engineers, and cybersecurity specialists far exceeds supply, with 250,000 person shortage in data scientists alone.
This scarcity inflates compensation, extends recruitment timelines, and forces organizations to compete with tech giants for limited talent pools.
How Companies Address It: Transformation companies supplement internal capabilities with their own talent pools, providing immediate access to specialists without lengthy recruitment. They implement knowledge transfer programs where consultants work side-by-side with client teams, building internal capabilities through hands-on collaboration.
Reskilling and upskilling initiatives help existing employees develop digital capabilities. Organizations investing in continuous learning see 5.3x higher success rates than technology-only approaches. Training programs, certifications, and learning platforms democratize digital skills across organizations.
Low-code and no-code platforms enable business users with limited programming skills to build applications and automate workflows, reducing dependence on scarce developer resources.
Challenge 3: Cultural Resistance and Change Management Failures
The Problem: Cultural and organizational barriers dominate transformation challenges, exceeding technology obstacles. Employees fear job displacement, resist changing familiar workflows, and question transformation necessity. Middle management often becomes transformation bottlenecks when they perceive threats to their roles.
Research shows that 70% of transformation projects fail, with inadequate change management as a leading cause. Organizations that implement formal change management strategies are 7x more likely to meet transformation goals.
How Companies Address It: Successful transformation companies emphasize that digital transformation is fundamentally a people challenge requiring structured change management.
Communication strategies articulate clear vision, explain “what’s in it for me” for different stakeholder groups, and celebrate progress. Transparency about job impact—whether redeployment, upskilling, or new roles—reduces uncertainty and anxiety.
Stakeholder engagement identifies champions who advocate for transformation, influencers who shape opinions, and resistors requiring special attention. Building coalitions of support across organizational levels creates momentum that overcomes pockets of resistance.
Early involvement of end users in design and pilot phases increases buy-in. When people participate in shaping solutions rather than having them imposed, adoption improves dramatically.
Training and enablement ensure people feel confident using new systems. Comprehensive programs include role-based training, job aids, and ongoing support through help desks or super-user networks.
Challenge 4: High Costs and Budget Constraints
The Problem: 26% of leaders cite high or unforeseen costs as major transformation challenges. Digital transformation requires substantial investment—global spending reached $2.5 trillion in 2024 and will hit $3.9 trillion by 2027. 24% report economic uncertainty affecting budgets, forcing difficult prioritization decisions.
Projects frequently exceed initial estimates due to scope creep, unexpected integration complexity, or prolonged timelines. Failed transformations cost organizations an average 12% of annual revenue.
How Companies Address It: Transformation companies implement phased approaches that sequence initiatives by value and feasibility. Quick wins generating early ROI fund subsequent phases, creating self-funding transformation programs.
Value-effort matrices prioritize initiatives delivering maximum business impact with minimum effort, ensuring limited budgets focus on highest-return activities.
Agile delivery with 2-4 week sprints enables continuous value delivery and course correction. Rather than investing millions in 18-month waterfall projects, organizations see tangible progress every sprint with opportunities to adjust priorities.
Cost-efficient delivery models leverage offshore and nearshore resources for activities not requiring on-site presence. This can reduce expenses 30% or more compared to equivalent domestic resources.
Challenge 5: Lack of Clear Strategy and Executive Alignment
The Problem: 20% cite lack of strategy around digital initiatives while 13% report lack of senior-level support as transformation obstacles. Without clear vision and sustained executive commitment, initiatives devolve into disconnected technology projects that fail to deliver business value.
Leadership misalignment—where different executives pursue competing priorities—fragments effort and prevents coordinated transformation.
How Companies Address It: Transformation begins with strategy development that articulates clear vision, defines success metrics, and aligns technology roadmaps with business objectives. This creates shared understanding across leadership.
Executive sponsorship programs prepare C-suite leaders to fulfill critical responsibilities throughout transformation—active participation, coalition building, and consistent communication. Research consistently identifies sponsorship as the top contributor to transformation success.
Governance structures establish decision-making frameworks, resolve conflicts, and maintain alignment as transformations progress. Regular steering committee meetings ensure leadership stays engaged and addresses obstacles quickly.
👉 Pro Tip: Resistance to transformation often stems from fear rather than opposition. When you encounter pushback, dig deeper to understand underlying concerns. Is it job security? Comfort with familiar processes? Lack of skills to succeed in a new environment? Addressing root causes directly—through transparent communication, training, and transition support—transforms resistors into advocates.
Why 70% of Digital Transformations Fail (And How to Succeed)
Understanding why initiatives fail is essential—and a digital transformation company helps convert risks into results. Most failures trace back to people, strategy, and scope, not technology.
Top 5 Reasons for Transformation Failure (and How a Digital Transformation Company Fixes Them)
-
Treating Transformation as IT-Only
-
Risk: When IT runs solo, solutions miss business needs and adoption stalls.
-
Fix: A digital transformation company elevates it to a CEO-led program with business, finance, operations, HR, and IT in one governance model.
-
No Formal Change Management
-
Risk: Without structured adoption, even great tech underperforms.
-
Fix: A digital transformation company pairs delivery with change plans, budgeting one dollar for adoption and training for every dollar on technology.
-
Vague or Misaligned Business Objectives
-
Risk: Teams can’t prioritize, measure, or sustain momentum.
-
Fix: A digital transformation company defines outcomes in business terms—revenue growth, cost reduction, CSAT, and time-to-market—then ties every initiative to clear KPIs.
-
Weak Executive Sponsorship
-
Risk: Multi-year programs stall without visible, active leaders.
-
Fix: A digital transformation company secures CEO sponsorship, sets cadence for decisions, and maintains executive communication to keep resources aligned.
-
Doing Too Much Too Fast
-
Risk: Enterprise-wide “big bang” overwhelms teams and burns budgets.
-
Fix: A digital transformation company sequences domains (e.g., a full customer journey), proving value end to end before scaling.
Success Patterns Used by a Digital Transformation Company
-
Start with Business Value
Focus on high-impact domains, not “shiny object” tools. Prioritize initiatives that drive measurable financial and customer outcomes. -
Build Multidisciplinary Teams
Blend business stakeholders, product, design, engineering, data, and change leaders. A digital transformation company integrates these roles to accelerate delivery and adoption. -
Measure Continuously
Track three layers: value (financial and operational KPIs), team health (productivity, skills, practices), and change progress (capability building, engagement, usage). -
Invest in Talent and Capabilities
Develop in-house skills alongside expert partners. A digital transformation company upskills your teams while delivering, so you can sustain momentum. -
Iterate and Learn
Adopt agile delivery with short cycles, real user feedback, and incremental releases. A digital transformation company avoids waterfall lock-in and pivots early when needed.
Pro Tip: When shortlisting a digital transformation company, ask for proof of outcomes: which KPIs moved, how ROI was measured, adoption rates achieved, and what they changed when early signals were weak.
Top Digital Transformation Companies to Consider in 2025
Choosing the right digital transformation company starts with understanding provider types: global consultancies, boutique specialists, and technology vendors that package services with platforms. Matching your needs to the right digital transformation company helps you accelerate value and reduce risk.
Global Consulting Firms
-
Accenture: A global digital transformation company operating in 120+ countries with 100+ innovation centers, delivering end-to-end programs from strategy to scaled implementation, backed by industry playbooks and top platform partnerships.
-
Deloitte Digital: A digital transformation company known for experience design and customer journey reinvention, with strong sector depth in retail, healthcare, financial services, and the public sector.
-
McKinsey Digital: A strategy-led digital transformation company focused on measurable business value, senior practitioner delivery, and executive alignment, often selected for board-level, complex transformations.
-
Capgemini: A technology-forward digital transformation company strong in AI, automation, and Industry 4.0; Capgemini Invent drives customer-centric innovation from core to edge.
-
Cognizant: A scale digital transformation company (500,000+ employees, 120+ countries) with strengths in app modernization, cloud enablement, intelligent automation, and data analytics across major industries.
Specialized Transformation Providers
-
HBLAB: A specialised digital transformation company with 10+ years of delivery and 630+ professionals. CMMI Level 3 quality, AI-powered solutions since 2017, and flexible engagement models (offshore, onsite, dedicated teams) make HBLAB a cost-efficient digital transformation company (often ~30% lower) for mid-market and enterprise needs across e‑commerce, fintech, healthcare, and logistics.
Technology Vendor Transformation Services
-
IBM iX: A design-led digital transformation company within IBM that blends AI, blockchain, and enterprise integration—often selected for regulated, large-scale programs in finance and healthcare.
-
Salesforce: A customer-first digital transformation company and platform ecosystem for marketing, sales, and service, enabling rapid CRM-led transformation with robust integration options.
Selection Criteria for Choosing the Right Partner
-
Industry Expertise: Choose a digital transformation company with demonstrated results in your sector and familiarity with regulatory nuances.
-
Technical Capabilities: Validate the digital transformation company’s depth in cloud, data, AI/ML, IoT, security, and integration—backed by case studies.
-
Cultural Fit: Ensure the digital transformation company’s collaboration style, communication cadence, and values align with your teams.
-
Geographic Presence: Balance onsite support with cost efficiency; many digital transformation companies mix local leadership with offshore delivery.
-
Size and Scale: Large digital transformation companies offer breadth and speed; boutiques offer focus and partner-level attention. Match scale to scope.
-
References and Case Studies: Ask the digital transformation company for outcomes, metrics, adoption rates, and lessons learned—not just logos.
👉 Pro Tip: When shortlisting a digital transformation company, prioritise evidence of business outcomes over brand prestige. Ask: Which KPIs did you move? How do you measure ROI and adoption? What percent of programs met objectives, and why?
Emerging Technologies Shaping Digital Transformation in 2025
The technology landscape evolves rapidly, with new capabilities creating transformation opportunities while obsoleting older approaches. Understanding emerging trends helps organizations future-proof investments.
Generative AI and Large Language Models
Generative AI has exploded into mainstream business consciousness following ChatGPT’s late 2022 launch. The technology generates human-like content—text, images, code, audio—from prompts, enabling new productivity paradigms.
Business Applications: Content creation for marketing, code generation accelerating software development, customer service chatbots providing natural conversations, document analysis and summarization, and personalized recommendations.
The generative AI market is projected to grow from $137 billion in 2024 to $1.3 trillion within the next decade, representing one of the fastest technology adoptions in history. 77% of companies are leveraging AI within their business operations.
Strategic Considerations: While potential is enormous, generative AI requires careful implementation. Organizations must address data privacy, bias mitigation, accuracy verification, and ethical considerations. Starting with well-defined use cases delivering clear business value prevents “AI for AI’s sake” experiments that waste resources.
Agentic AI and Autonomous Systems

Agentic AI represents the next evolution—systems that operate autonomously to achieve objectives without constant human oversight. Unlike current AI tools requiring user prompts, agentic systems plan, act, learn, and adapt independently.
The agentic AI market is projected to reach $30.89 billion in 2024 with 31.68% CAGR, signaling rapid enterprise adoption. Applications include autonomous supply chain optimization, self-healing IT infrastructure, intelligent process automation, and adaptive customer engagement.
This shift from AI as tool to AI as agent fundamentally changes how organizations design operations, potentially automating entire workflows that currently require human coordination.
Edge Computing and 5G Connectivity
Edge computing processes data closer to where it’s generated rather than sending everything to centralized cloud data centers. This reduces latency, improves real-time responsiveness, and addresses bandwidth constraints.
5G networks provide the high-speed, low-latency connectivity that enables edge applications to flourish. Together, these technologies enable real-time analytics for IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, augmented reality experiences, and industrial automation.
Manufacturing plants use edge computing to analyze sensor data from production lines in milliseconds, enabling immediate adjustments that improve quality and reduce waste. Retail stores process customer behavior analytics at the edge to trigger personalized promotions instantly.
Blockchain for Trust and Transparency
- Blockchain technology has evolved far beyond cryptocurrency origins to become enterprise infrastructure for trusted transactions, supply chain transparency, and decentralized business models.
- Supply chain applications provide end-to-end traceability—tracking products from raw materials through manufacturing to final delivery. This enables authenticity verification, quality assurance, and rapid issue resolution when problems occur.
- Financial services use blockchain for faster cross-border payments, automated contracts (smart contracts), and regulatory compliance. Healthcare explores blockchain for secure health information exchange and drug supply chain integrity.
Internet of Things (IoT) at Scale
IoT deployments continue accelerating with sensors embedded in products, equipment, buildings, and infrastructure. The data these devices generate enables predictive maintenance, usage-based business models, and operational optimization.
- Manufacturing uses IoT for equipment monitoring that predicts failures before they occur, scheduling maintenance during planned downtime and avoiding costly unplanned outages. Transportation and logistics track shipments in real-time, optimizing routes and providing customers with accurate delivery estimates.
- Smart cities leverage IoT for traffic optimization, energy management, public safety, and citizen services. Seoul, South Korea leads in 5G-enabled smart city initiatives reducing traffic congestion and improving safety through real-time monitoring.
Quantum Computing on the Horizon
Quantum computing remains emerging but promises revolutionary capabilities for optimization problems, cryptography, drug discovery, and financial modeling. While practical business applications are still years away, forward-thinking organizations monitor progress to understand implications.
Quantum computers may eventually break current encryption methods, requiring quantum-resistant cryptography. They could optimize supply chains, portfolio management, and logistics at scales impossible for classical computers.
Organizations don’t need immediate quantum strategies but should track developments to avoid being blindsided by sudden advances.
Low-Code/No-Code Platforms
Low-code and no-code platforms democratize application development, enabling business users with limited programming skills to build applications and automate workflows. This addresses developer scarcity while empowering business teams to solve problems directly.
Organizations use these platforms for rapid prototyping, departmental applications, workflow automation, and legacy system modernization. Citizen developers create solutions 5-10x faster than traditional coding approaches for appropriate use cases.
Strategic application development still requires professional developers, but low-code platforms handle routine needs that would otherwise create IT backlogs.
Digital Transformation Across Industries: Sector-Specific Insights
While digital transformation principles apply universally, implementation varies significantly by industry due to unique regulations, business models, and competitive dynamics.
Financial Services and Banking
- Digital banking platforms have transformed how consumers interact with financial institutions. Traditional banks have launched mobile-first offerings competing with neobanks and fintech startups.
- Goldman Sachs launched “Marcus” in 2016, moving much of its financial services online. This enabled better data collection for understanding customers, market trends, and offering custom products. The bank now uses AI and machine learning to analyze vast data for improved predictions and analysis.
- Capital One invested heavily in smartphone app capabilities, integrating security features like Touch ID. This lowered costs by empowering customer self-service while gathering data enabling more personalized marketing.
- Key Technologies: Mobile banking apps, AI for fraud detection, blockchain for payments, open banking APIs, chatbots for customer service, and robotic process automation for back-office operations.
Healthcare and Life Sciences

- Healthcare digital transformation focuses on improving patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and research acceleration while navigating strict regulatory requirements like HIPAA.
- Telemedicine platforms expanded dramatically during COVID-19, enabling remote consultations that improve access while reducing costs. Electronic health records (EHR) centralize patient information, improving care coordination across providers.
- AI applications include diagnostic imaging analysis, drug discovery acceleration, personalized treatment recommendations, and operational optimization.
- Key Challenges: Data privacy and security, interoperability between systems, regulatory compliance, and change management with clinical staff.
Retail and E-Commerce
- Omnichannel experiences blur lines between physical and digital shopping, enabling customers to browse online and pick up in-store, return online purchases to physical locations, and receive personalized recommendations across channels.
- Amazon Business exemplifies B2C companies extending to B2B markets, offering 250+ million products with analytics tools and guided buying for business purchasers. Walmart invested heavily in technology enabling grocery pickup, delivery, supply chain optimization, and robotics—competing effectively against Amazon.
- IKEA uses augmented reality to enable customers to visualize furniture in their homes before purchasing, reducing returns and improving satisfaction.
- Key Technologies: E-commerce platforms, mobile shopping apps, AI for personalization, AR/VR for product visualization, IoT for inventory management, and data analytics for demand forecasting.
Manufacturing and Industrial

- Smart manufacturing leverages IoT sensors, AI analytics, and automation to optimize production, predict equipment failures, and improve quality.
- General Electric (GE) transformed manufacturing processes using 3D printing, computer-assisted design, and Industrial IoT. AI and data analytics study product performance, driving continuous enhancement.
- Digital twins—virtual replicas of physical assets—enable simulation and optimization before implementing changes in real production environments.
- Key Technologies: IoT sensors and connected equipment, AI for predictive maintenance, robotics and automation, digital twins, edge computing for real-time analytics.
Transportation and Logistics
- DHL uses AI and machine learning to analyze data from its global carrier network, continuously optimizing complex logistics operations. AI-powered chatbots reduce labor costs while enabling customers to easily access shipment information.
- Fleet management systems use IoT telematics to track vehicles, optimize routes, monitor driver behavior, and schedule maintenance.
- Autonomous vehicles and drones represent emerging capabilities for last-mile delivery and warehouse operations.
- Key Technologies: Route optimization algorithms, real-time tracking systems, predictive analytics, autonomous vehicles, warehouse automation, and blockchain for supply chain transparency.
When to Engage a Digital Transformation Company vs. Building Internal Capabilities
Organizations face strategic decisions about whether to partner with external transformation companies, build internal capabilities, or pursue hybrid approaches. Multiple factors influence this choice.
Scenarios Favoring External Partners
Complex, Enterprise-Scale Transformations: Organizations pursuing comprehensive transformations affecting multiple business units and requiring diverse expertise benefit from external partners who bring cross-functional teams and proven methodologies.
- Time-Sensitive Initiatives: When competitive pressure or market disruption demands rapid transformation, external partners accelerate timelines through pre-built assets, larger teams, and elimination of learning curves.
- Specialized Technology Requirements: Emerging technologies like AI, blockchain, or advanced analytics require specialized skills that are expensive and time-consuming to develop internally. Partnering provides immediate access to scarce expertise.
- Limited Internal Resources: Organizations with small IT teams or constrained budgets may lack capacity to execute transformation while maintaining day-to-day operations. External partners provide supplemental capacity without permanent headcount increases.
- Objective Assessment Needed: When internal politics, legacy assumptions, or organizational blindspots constrain innovation, external partners provide unbiased perspectives and can champion necessary changes without career risk.
Scenarios Favoring Internal Development
- Proprietary Differentiation: When transformation involves core competencies that create competitive advantage, organizations may prefer developing capabilities internally to maintain proprietary control.
- Ongoing, Continuous Transformation: Digital transformation is not a one-time project but continuous evolution. Organizations planning multi-decade digital journeys need internal capabilities to sustain momentum without permanent external dependencies.
- Sufficient Internal Expertise: Organizations with strong technology teams, prior transformation experience, and deep industry knowledge may execute effectively without external support.
- Budget Constraints: While external partners often provide better value than building equivalent internal capabilities, organizations facing severe budget limitations may need to pursue slower, incremental transformation using existing resources.
- Sensitive Data or Regulatory Constraints: Industries with strict data privacy requirements or national security concerns may face restrictions on sharing information with external parties.
Recommended Hybrid Approach
Most successful transformations combine external and internal resources strategically:
- Strategy and Architecture: Engage external partners for initial strategy development, architecture design, and roadmap creation—leveraging their cross-industry experience and proven frameworks.
- Implementation: Use hybrid teams combining external specialists with internal staff for implementation. This transfers knowledge while maintaining momentum.
- Capability Building: Structure engagements to emphasize knowledge transfer, training, and internal capability development so external dependencies decrease over time.
- Ongoing Operations: Transition to internal teams for steady-state operations, support, and incremental improvements after major implementations complete.
Specialized Expertise: Maintain relationships with external partners for specialized needs—emerging technologies, complex integrations, or surge capacity during major initiatives.
Accelerate your digital transformation journey!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the digital transformation of a company?
A digital transformation company helps rewire how a company operates by integrating digital technology across all functions to improve value delivery, customer experience, and growth. It moves beyond digitizing tasks to drive new business models, cultural change, and continuous tech deployment at scale with measurable outcomes.
2. What are the 4 types of digital transformation?
A digital transformation company typically scopes four types: 1) Business Process Transformation (automation and efficiency), 2) Business Model Transformation (new digital revenue/value), 3) Domain Transformation (reimagining areas like service or supply chain), and 4) Cultural/Organizational Transformation (skills, mindsets, agile ways of working). These often overlap in a cohesive roadmap.
3. Why does 70% of digital transformation fail?
A digital transformation company sees failure when change management is weak, strategy is unclear, executive sponsorship is thin, teams treat it as “IT-only,” or scope is too broad too fast. Strong change management, value-led roadmaps, and active leadership dramatically improve success and reduce wasted spend.
4. What is an example of a company that went through digital transformation?
Netflix is a model case a digital transformation company might cite: shifting from DVDs to streaming, investing in cloud, delivery networks, and recommendation engines to reinvent the business model and customer experience—not just digitize legacy processes.
5. What are the 4 pillars of digital transformation?
A digital transformation company typically frames four pillars: 1) Technology (cloud, AI, analytics), 2) Data (governance, quality, insight), 3) Process (workflow optimization, automation), and 4) People (skills, culture, readiness). Neglecting the people pillar is a frequent reason initiatives stall.
6. What are the 5 types of digital transformation?
A digital transformation company may extend to five types by adding Customer Experience Transformation to the four-core model: process, business model, domain, cultural, and CX transformation. Many programs also track progress through five maturity stages from Traditional to Transformational.
7. What are the 7 pillars of digital transformation?
When expanded, a digital transformation company may align to seven pillars: Customer Experience, Operational Processes, Business Models, Technology, Data, People & Culture, and Leadership/Governance. The number matters less than addressing tech, business, organizational, and human levers together.
8. What are the 10 emerging technologies?
A digital transformation company will highlight: 1) Generative AI, 2) Agentic AI, 3) Advanced connectivity (5G+), 4) Edge computing, 5) IoT at scale, 6) Blockchain, 7) Quantum computing, 8) AR/VR, 9) Robotics/hyperautomation, 10) Digital twins. These combine (e.g., 5G + IoT + AI) to unlock real-time, data-driven value.
9. What is digital transformation in one word?
A digital transformation company would say “adaptation”—the ongoing adaptation of operations, culture, and capabilities to leverage evolving digital tech for advantage. “Rewiring” also fits the enterprise-wide scope.
10. Is AI a digital transformation?
AI isn’t the whole; a digital transformation company treats AI as a critical enabler within a broader business transformation. The mandate is to connect AI to clear business value—cost, speed, quality, and customer outcomes—rather than “AI for AI’s sake.”
11. How do you start a digital transformation?
A digital transformation company starts with: 1) CEO-backed sponsorship, 2) Maturity assessment, 3) Business-outcome targets, 4) Phased roadmap (quick wins + big bets), 5) Cross-functional teams, 6) Domain focus (end-to-end journeys), and 7) Equal investment in change management and training.
12. Is digital transformation a skill?
A digital transformation company builds a portfolio of skills: strategy and value mapping, change leadership, cloud/data/AI literacy, product and project delivery, stakeholder management, and continuous learning. It’s a team sport—not a single role—and the best teams blend business acumen with technical depth.
HBLAB – Your Trusted Digital Transformation Partner
With 10+ years of experience and a team of 630+ professionals, HBLAB provides expert digital transformation services and custom software development solutions tailored to your business objectives. We hold CMMI Level 3 certification, ensuring high-quality processes throughout every engagement, and have been at the forefront of AI-powered solutions since 2017, bringing deep expertise in emerging technologies when you need them most.
Our flexible engagement models—offshore, onsite, and dedicated teams—combined with cost-efficient services (often 30% lower cost than domestic alternatives) help businesses worldwide accelerate digital transformation projects without compromising quality. Whether you need to modernize legacy systems, migrate to cloud infrastructure, implement AI-driven automation, or build custom applications, HBLAB’s senior talent pool (over 60% with 5+ years experience) delivers solutions that drive measurable business value.
We specialize in comprehensive digital transformation services including cloud migration strategy and implementation, AI/ML integration for predictive analytics and intelligent automation, enterprise application development and modernization, data platform architecture and analytics, and full-cycle software development with agile methodologies.
Our track record spans successful implementations for clients in e-commerce, fintech, healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific markets.
Contact HBLAB for a free consultation
Read More:
– AI and Machine Learning Trends 2025: The Solid Basis for Enterprise Transformation
– High Tech Manufacturing: The Future of Advanced Production and Quality Excellence in 2025
– Legacy Application Modernization: A Complete Guide for 2025