Data security solutions represent a comprehensive framework of technologies, processes, and practices designed to protect sensitive information throughout its entire lifecycle. Unlike traditional security approaches that focus solely on perimeter defense, modern data security solutions operate on a principle of continuous verification and multi-layered protection across all data states: at rest in storage systems, in transit across networks, and in use during active processing.
Understanding the Core Architecture of Data Security Solutions
The foundation of any effective data security solution rests on eight interconnected components that work together to create a resilient protective environment:
Data Discovery and Classification forms the starting point, automatically identifying and categorizing sensitive information such as personally identifiable information (PII), financial records, intellectual property, and health data.
Encryption serves as the fundamental protective mechanism, rendering data unreadable to unauthorized parties whether stored on devices or transmitted across networks using protocols like TLS and IPsec.
Identity and Access Managementensures that only verified users with appropriate permissions can access specific data assets, implementing the principle of least privilege that grants individuals only the minimum access required for their roles.
Threat Protection mechanisms including firewalls and intrusion prevention systems identify and block malicious activities before they compromise data integrity.
Monitoring and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platforms provide real-time visibility into security events by collecting and analyzing logs from multiple sources to detect anomalies and potential breaches.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools prevent unauthorized data exfiltration by monitoring and controlling data movement to external destinations.
Backup and Disaster Recovery capabilities create immutable copies of data that remain inaccessible to ransomware attacks, enabling rapid recovery even after successful intrusions.
Cyber Resilience measures incorporating Zero Trust architecture and automated recovery mechanisms ensure organizations can maintain operations and restore normal function following security incidents.
What distinguishes modern data security solutions from older approaches is their integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies enable real-time threat detection that identifies anomalous behavior and attack patterns far faster than manual security operations. The shift reflects a fundamental understanding that cybersecurity professionals cannot outpace the volume and sophistication of modern attacks without automation-driven intelligence.
The Five Pillars and Practical Security Controls Framework
Organizations implementing data security solutions must understand two distinct but complementary frameworks: the Five Pillars of Information Security that define protection objectives, and the Five Types of Security Controls that describe implementation mechanisms.
The Five Pillars of Information Security
The Five Pillars establish what must be protected:
- Confidentiality ensures data remains accessible only to authorized users through access controls and encryption
- Integrity verifies that data has not been altered or corrupted through hashing, digital signatures, and version control
- Availability guarantees that authorized users can access necessary data when required through redundant systems and disaster recovery
- Authenticity confirms the true identity of data sources and users through authentication mechanisms
- Non-Repudiation prevents users from denying their involvement in transactions through digital signatures and audit logs
The Five Types of Security Controls
The Five Types of Security Controls describe how organizations implement protection at different points in the attack lifecycle:
Preventive Controls stop incidents before they occur through measures like firewalls that block malicious traffic, multi-factor authentication that prevents unauthorized access, and encryption that renders data unreadable.
Detective Controls identify incidents when they happen or shortly after through security monitoring, intrusion detection systems, and log analysis that reveal unauthorized activities.
Corrective Controls repair systems after incidents through patch management, incident response procedures, and immutable backup restoration that eliminates ransomware from infected files.
Deterrent Controls discourage potential threats through visible security measures and organizational policies that signal protective intent.
Compensating Controls provide alternative safeguards when primary protections are unavailable through manual processes or backup systems that reduce overall risk.
Effective data security solutions implement all control types working together in defense-in-depth architecture.
A practical example illustrates this layered approach: preventing insider data theft combines preventive controls (DLP policies blocking file transfers to personal cloud storage), detective controls (behavioral analytics identifying abnormal data access patterns), deterrent controls (security awareness training and acceptable use policies), and corrective controls (incident response procedures and account restrictions).
GDPR’s Seven Data Protection Principles
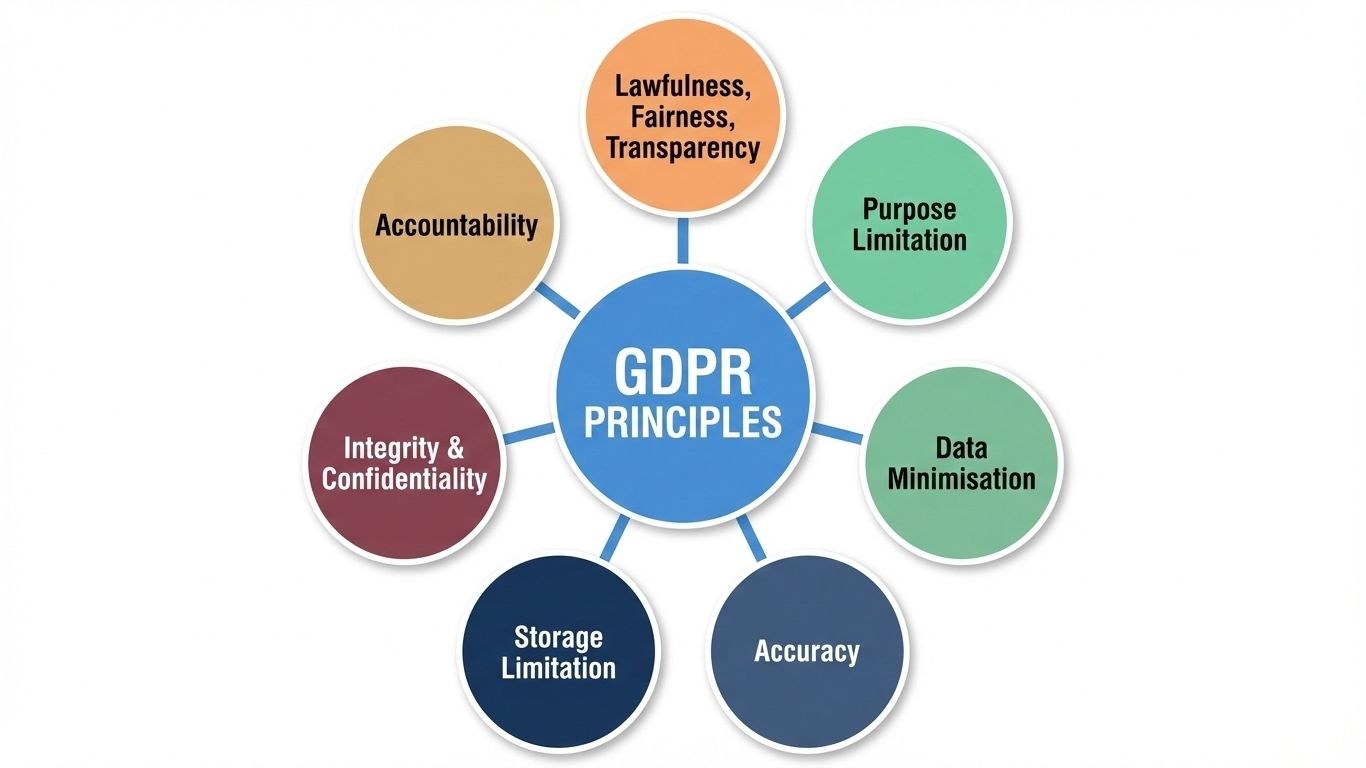
The GDPR’s Seven Data Protection Principles provide regulatory guidance that fundamentally shaped data security solution design. These principles, applicable across industries whenever personal data is processed, establish that data handling must be:
- Lawful, Fair, and Transparent (requiring documented justification for processing)
- Limited to stated Purpose
- Minimized to only necessary data
- Kept Accurate
- Retained only as long as needed
- Protected through Integrity and Confidentiality measures
- Subject to Accountability through documented compliance
Practical Implementation: Selection, Deployment, and Operational

Best Practices
Organizations evaluating data security solutions face distinct pathways depending on their maturity, regulatory environment, and operational complexity. The selection process begins with baseline assessment: identify where sensitive data resides, which systems require protection, what regulatory requirements apply, and what security gaps currently exist.
Evaluation Framework
The evaluation of potential solutions requires weighted scoring across multiple dimensions:
- Technical capabilities (40%): data discovery automation, encryption strength, API integrations
- Vendor experience (25%): proven track record in your specific industry and deployment environment
- Total cost of ownership (20%): licensing, implementation, training, ongoing support
- Integration depth (10%): compatibility with existing security tools and IT infrastructure
- Compliance certifications (5%): audit readiness and regulatory alignment
This framework prevents organizations from defaulting to lowest-cost options while overlooking critical functionality gaps.
Phased Implementation Approach
Implementation follows a phased approach that prevents operational disruption while progressively strengthening security posture.
Initial phases focus on high-value, high-risk assets such as systems storing financial data or customer information.
Middle phases extend protection to additional systems while establishing operational procedures and training.
Final phases encompass comprehensive monitoring, continuous improvement, and advanced features like behavioral analytics.
Each phase includes testing, stakeholder feedback, and refinement before advancing.
The Human Factor
The practical reality of implementation reveals that technology represents only one component of success. Employee training proves equally critical because human error remains the leading cause of data breaches.
Effective training covers:
- Data classification
- Secure file sharing
- Recognition of phishing attempts
- Password hygiene
- Incident reporting
Organizations that build security awareness into company culture experience significantly lower breach rates and insider threat incidents than those treating training as a compliance checkbox exercise.
Cloud-Delivered Security Solutions
For organizations with constrained resources, particularly small and medium businesses, cloud-delivered security solutions offer advantages. Cloud-native platforms eliminate upfront hardware investments, provide automatic updates as threats evolve, and scale capacity based on data volume growth.
Managed security service providers extend this model further by outsourcing security operations entirely, allowing internal teams to focus on core business activities while external experts manage 24/7 threat monitoring and response.
Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture represents the modern framework reshaping data security solution design across enterprise environments. Rather than assuming users and devices within the corporate network deserve trust, Zero Trust requires continuous verification of every access request regardless of location or user identity.
This principle proves especially relevant in hybrid and remote working environments where traditional network perimeters dissolve. Implementation involves:
- Multi-factor authentication that verifies user identity
- Device posture checks confirming endpoint security
- Micro-segmentation that isolates critical resources
- Real-time monitoring that detects anomalous behavior
Five Fundamental Protective Measures
The simplest approach to protecting data across all organization sizes begins with five fundamental protective measures:
- Creating strong, unique passwords for each system and account
- Installing and maintaining current antivirus and endpoint protection software
- Enabling encryption for both stored data and network transmission
- Implementing multi-factor authentication on systems accessing sensitive information
- Maintaining regular data backups in geographically separate locations
Advanced Implementation Frameworks
Organizations establishing mature data security operations recognize that technology selection represents only the starting point. Operational excellence requires governance frameworks, continuous improvement processes, and cultural changes supporting security objectives.
Least Privilege Access Control
Least Privilege Access Control fundamentally changes how organizations manage data permissions. Rather than granting broad access that individuals might eventually need, least privilege starts with minimal permissions and grants additional access only when business processes require it.
Implementation proceeds through:
- Assessment of existing permissions to identify over-provisioned accounts
- Policy definition establishing criteria for access grants and revocations
- Enforcement through identity and access management tools like JumpCloud or Okta that enforce role-based and attribute-based policies
- Continuous monitoring of access patterns and anomalies
- Regular audits confirming that access levels remain appropriate as roles evolve
Just-in-time access models extend this concept further, providing elevated privileges only when needed and for limited durations, requiring re-authentication when access is requested.
Zero Trust Security Architecture
Zero Trust security architecture represents the modern standard reshaping enterprise security strategies. Rather than assuming users and devices within corporate networks deserve implicit trust, Zero Trust operates on the principle that every access request requires explicit verification regardless of source.
Implementation involves:
- Verifying user identity through multi-factor authentication that prevents credential-based attacks
- Confirming device security posture including current patches and antivirus status
- Enforcing least privilege access limiting users to specific resources rather than broad network access
- Encrypting all communications end-to-end ensuring that network monitoring cannot reveal data
- Maintaining continuous monitoring that detects compromise or unusual behavior requiring immediate response
Organizations adopting Zero Trust report significantly reduced breach severity because attackers cannot move laterally once inside the network perimeter, as each resource access requires re-authentication and explicit authorization.
SIEM Implementation
SIEM implementation represents a critical operational capability that many organizations underestimate in complexity. Deployment requires:
- Identifying all data sources including network devices, applications, databases, and security tools
- Configuring log collection and standardization ensuring consistent format and timestamp correlation
- Defining detection rules tailored to your specific threat environment and risk profile
- Tuning alert thresholds to minimize false positives that generate investigation fatigue
- Maintaining threat intelligence integration that automatically updates as new attack patterns emerge
- Establishing incident response processes that specify how teams will investigate and remediate detected events
Security Frameworks
Security frameworks provide the roadmap that prevents tactical security decisions from contradicting strategic objectives:
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework emphasizes five parallel functions: Identify your assets and risks; Protect through implementation of safeguards; Detect intrusions and anomalies; Respond to identified incidents; and Recover from security events.
- ISO/IEC 27001 provides comprehensive requirements for information security management systems, serving as the international standard for certification.
- CIS Controls offer a prioritized list of essential actions, with the foundational CIS Implementation Group 1 covering basic controls that every organization should deploy.
- SOC 2 audits verify that organizations meet specific controls regarding security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
Selecting appropriate frameworks depends on your industry, regulatory environment, and organizational maturity, with many organizations starting with NIST while international operations typically require ISO 27001 alignment.
Compliance Automation
Compliance automation has become essential for organizations managing multiple jurisdictional requirements. Solutions like Securiti.ai automate compliance mapping, showing how specific technical controls satisfy regulatory requirements across GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and emerging regulations.
Rather than manual tracking of compliance obligations, automation ensures policies adapt as regulations change and provides evidence demonstrating compliance during audits.
Security Effectiveness Metrics
The measurement of data security effectiveness increasingly relies on metrics rather than subjective assessments:
Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) measures how quickly security operations identify breaches, with industry benchmarks suggesting detection within days rather than months.
Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) measures incident response speed, critical because faster containment dramatically reduces breach impact.
Security metrics should also track:
- Data discovery coverage percentages
- Encryption adoption rates across data classifications
- Access review completion rates
- Vulnerability remediation timelines
Practical Implementation Checklist for Data Security Solutions
- Begin by conducting baseline assessment of current security posture, identifying sensitive data locations and regulatory requirements.
- Select solutions addressing your highest-priority risks first rather than attempting comprehensive implementation simultaneously.
- Pilot solutions in controlled environments before enterprise-wide deployment.
- Invest equally in employee training and technology because behavioral change proves as important as technical controls.
- Implement continuous monitoring and measurement, reviewing effectiveness quarterly and adjusting based on emerging threats.
- Establish board-level governance ensuring data security aligns with and supports business objectives rather than imposing unrelated constraints.
- Maintain flexibility in your approach, recognizing that data security operates in constantly evolving threat environment requiring continuous learning and adaptation.
ABOUT HBLAB
Selecting data security solutions is only the start. Successful outcomes depend on disciplined delivery, secure engineering practices, and teams that can integrate encryption, IAM, SIEM, DLP, and recovery into a coherent program.
HBLAB supports security critical initiatives with CMMI Level 3 certified processes that strengthen governance, documentation, and change control for data security solutions.

With 700 plus IT professionals and a strong senior talent ratio, HBLAB can deliver complex integrations and custom software that operationalize cloud data security solutions, endpoint data security solutions, and compliance aligned controls.
Enterprise grade security safeguards and IP protection help organizations implement a data security and privacy solutions guide in real environments without slowing product delivery.
With 10 plus years in custom digital solutions and cost efficient delivery compared to local rates, HBLAB helps IT leaders scale implementation while protecting budget for the core platforms and licenses.
People also ask
1. What are data security solutions?
Data security solutions are the technologies, processes, and policies used to protect sensitive data across its lifecycle by discovering it, controlling access to it, encrypting it, monitoring for abuse, preventing leaks, and ensuring recoverability after incidents.
In practice, data security solutions typically combine data discovery and classification, encryption, IAM and least privilege, threat protection, monitoring and SIEM, DLP, and backup and disaster recovery.
2. What are the three types of data security?
A practical way to group data security solutions is by protecting data in three states: data at rest, data in transit, and data in use.
This framing helps align controls such as storage encryption for data at rest and TLS for data in transit.
3. What is the best data security company?
There is no single best vendor for all organizations, because the best data security solutions depend on your data types, cloud stack, compliance scope, and operational maturity.
For commercial evaluation, common shortlists include major platform and specialist providers such as Microsoft, IBM, Varonis, Fortinet, Cohesity, and Thales, then selecting based on fit for your specific use cases like DLP, SIEM, encryption and key management, or ransomware recovery.
4. What are the 5 types of data security control?
The five types of security controls used inside data security solutions are preventive, detective, corrective, deterrent, and compensating controls.
This model ensures controls exist before an incident, during detection, and after containment and recovery.
5. What are the 4 types of security?
A useful way to describe security in modern data security solutions is the four layer security architecture: presentation layer, application layer, domain or network layer, and infrastructure layer.
This helps IT leaders assign ownership and controls across UI and API access, application security, segmentation and network defenses, and hardened infrastructure and logging.
6. What are 5 ways to secure data?
Five high impact actions that map cleanly to data security solutions are enabling MFA, encrypting sensitive data, enforcing least privilege access, keeping systems patched, and maintaining reliable backups.
This combination reduces credential abuse, limits blast radius, and supports fast recovery after ransomware or accidental deletion.
7. What are the 7 golden rules of data protection?
A widely used set of seven rules are the GDPR data protection principles:
-
Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency.
-
Purpose limitation.
-
Data minimization.
-
Accuracy.
-
Storage limitation.
-
Integrity and confidentiality.
-
Accountability.
8. What are the 5 pillars of data security?
A practical five pillar model used in data security solutions is confidentiality, integrity, availability, authenticity, and non repudiation.
These pillars translate directly into control choices such as access control for confidentiality, hashing and change control for integrity, resilience for availability, strong authentication for authenticity, and audit logging for non repudiation.
9. What is the simplest way to protect data?
If only one action can be taken, enabling multi factor authentication on key accounts is often the simplest high impact step because it blocks many password based attacks.
Right after that, automated backups provide the simplest safety net for loss and ransomware, and they integrate cleanly with broader data security solutions as you scale.
Read more:




