What is a RAG AI chatbot, is it important?
Artificial intelligence has fundamentally changed how enterprises manage knowledge. Yet, anyone who has deployed a standard large language model (LLM) knows the struggle: they hallucinate. They sound confident, but they often get the facts wrong. The RAG AI chatbot has emerged as the practical solution to this problem.
By combining the conversational fluency of generative AI with the factual precision of external data retrieval, this architecture allows technical teams to build bots that actually know their business. Technical leaders and developers are adopting the RAG-based AI chatbot to provide domain-specific answers without the massive expense of fine-tuning models. By integrating a retrieval mechanism, an AI chatbot with RAG ensures every response is grounded in verified, up-to-date information.
This guide analyzes the RAG framework, distinguishes it from standard AI approaches, and breaks down the engineering steps required to build a production-grade system.
What is RAG?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an architectural framework that optimizes an LLM’s output by referencing an authoritative knowledge base before generating a response.
Think of a traditional language model like a student taking a test from memory; if they don’t know the answer, they might guess. RAG changes the rules by allowing the student to open a textbook, find the specific paragraph, and answer based on that text.

The deeplearning AI RAG approach emphasizes that the model doesn’t need to memorize the world’s information. It just needs to understand how to process retrieved facts to formulate a coherent answer. This separation of reasoning and knowledge allows you to update your data in real time without ever touching the underlying machine learning models.
>> The Differences between RAG vs Fine-Tuning
What is a RAG AI Chatbot?
A RAG AI chatbot applies this framework specifically to conversational interfaces. While a standard AI generates text based on probability patterns learned during training, a RAG AI chatbot performs a search operation first.
When a user asks a question, the system queries a vector database to find content semantically related to that prompt. It combines the user’s question with these retrieved snippets and instructs the LLM to answer using only the provided context.
The result is an AI chatbot RAG system that cites its sources, minimizes fabrication, and handles proprietary company data securely. For enterprise use cases like customer support agents or internal legal assistants, this is the gold standard because it provides verifiable accuracy that purely generative models simply cannot match.
The Difference Between a RAG AI Chatbot and a Normal AI Chatbot
The primary distinction lies in memory and freshness. A normal AI chatbot, such as the base version of GPT-4 or Llama 3, relies entirely on parametric memory. This is the static information stored in its neural network weights during training. Once training is finished, that knowledge is frozen in time.
In contrast, a RAG AI chatbot utilizes non-parametric memory. It dynamically accesses external databases, PDFs, websites, or internal wikis in real time. While a normal chatbot might hallucinate an answer about a policy change that happened last week, a RAG-based AI chatbot retrieves the exact document explaining that policy and summarizes it.
Furthermore, a RAG AI chatbot offers transparency by providing citations. A normal AI cannot reliably verify where its specific answers came from.
The Difference Between an AI Chatbot and a Traditional Chatbot
To understand where we are, we have to look at where we came from. Traditional chatbots, often called rule-based or decision-tree bots, function on rigid scripts. They don’t truly “understand” language; they just scan for keywords. If a user deviates from the expected phrasing, the bot fails.
Conversely, an AI chatbot uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to comprehend intent, sentiment, and nuance. It generates novel responses rather than selecting from a list.
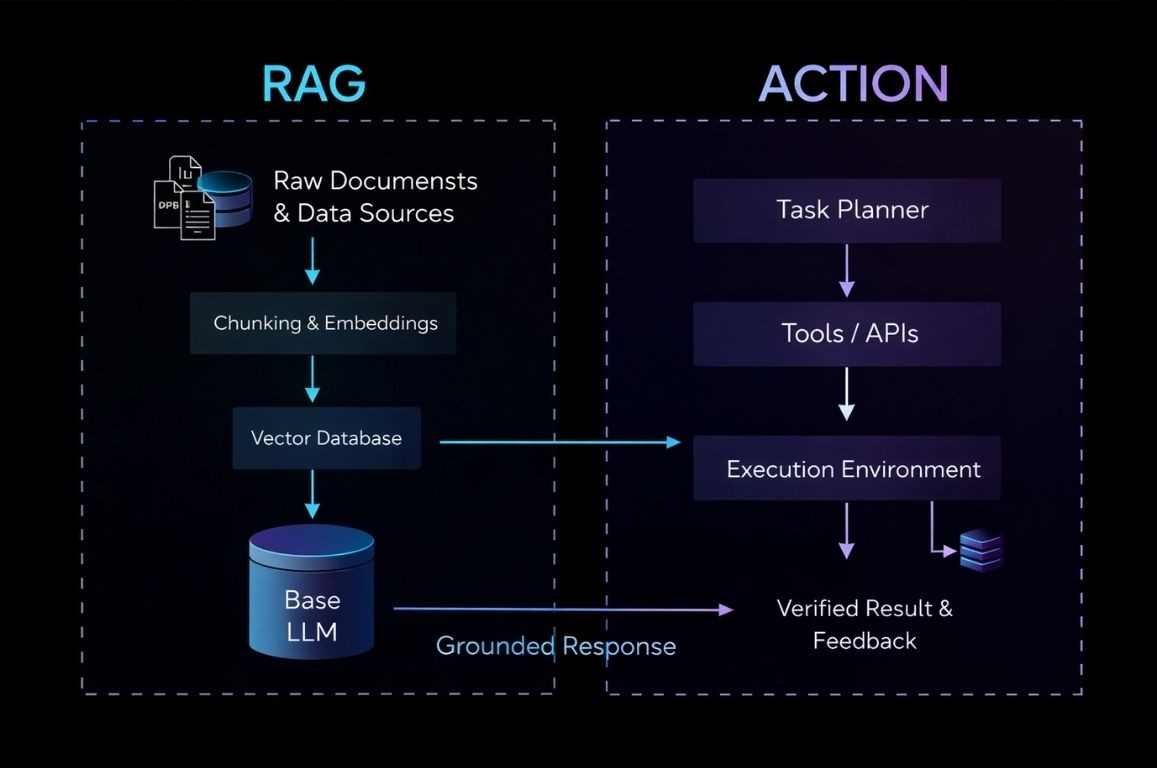
When we introduce the RAG AI chatbot, we combine the generative power of modern AI (similar to Agentic AI) with the strict adherence to facts found in traditional systems. It represents the best of both worlds: the flexibility of natural language understanding alongside the factual reliability of a curated knowledge base.
How to Build a Retrieval-Augmented Generation Chatbot
Building a production-grade RAG AI chatbot involves more than just connecting an API. It requires orchestrating a robust pipeline that moves data from raw documents to a generative response. This process relies on specific RAG AI tools and architectural patterns to ensure accuracy.
>> How to Deploy Large Language Models (LLMs)
The implementation generally follows a strict four-phase technical workflow: Ingestion, Retrieval, Generation, and Evaluation.
Phase 1: The ETL Pipeline (Ingestion & Indexing)
The foundation of any RAG-based AI chatbot is the quality of its knowledge base. Simply dumping documents into a model rarely yields results. The data must be processed for semantic understanding.
This begins with document loading. You use loaders from frameworks like LangChain or LlamaIndex to ingest proprietary data, whether it be PDFs, SQL databases, or HTML files. Tools like Unstructured.io are often necessary here to clean raw text and remove artifacts like headers or footers that might confuse the embedding model.
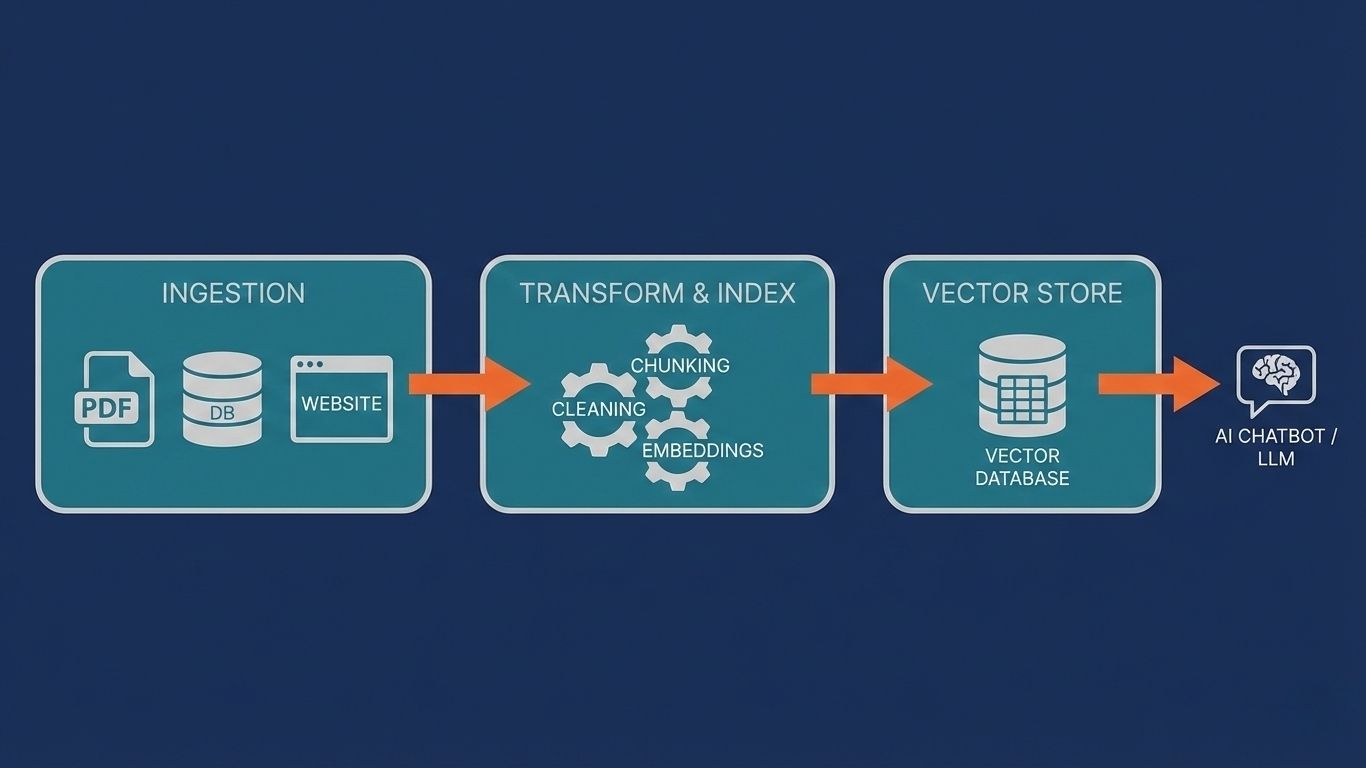
Once the data is loaded, you must implement a chunking strategy. This is perhaps the most critical step because Large Language Models have context window limits. You cannot feed a 100-page manual into a prompt all at once. Instead, you split the text into smaller segments, typically around 500 tokens.
It is best practice to include an “overlap” (e.g., 10-15%) between these chunks so that context isn’t lost at the boundaries of a split. Finally, these text chunks are converted into numerical vectors using an embedding model and stored in a Vector Database like Pinecone, Weaviate, or ChromaDB.
Phase 2: The Retrieval Engine
When a user asks a question, the RAG AI chatbot must find the “needle in the haystack.” The process often starts with query transformation. Users frequently ask vague questions, so the system should rewrite the query to improve search quality.
-
Example: Changing “How much is it?” to “What is the pricing for the Enterprise subscription?”
The system then performs the search. While a standard semantic search finds data based on meaning, a robust AI chatbot with RAG often utilizes Hybrid Search. This method combines vector search with traditional keyword search (BM25) to ensure that specific terms like part numbers or acronyms are not missed.
To further refine accuracy, successful architectures employ a Re-ranking step. After retrieving the top 10 results, a specialized model assesses which documents are actually most relevant, filtering out noise before the data ever reaches the LLM.
Phase 3: Augmentation and Generation
This phase is where the retrieved data meets the generative AI. The system takes the top-ranked data chunks and injects them into a system prompt. A typical prompt structure instructs the model to act as a helpful assistant and answer the user’s question using only the provided context, explicitly forbidding it from making up facts.
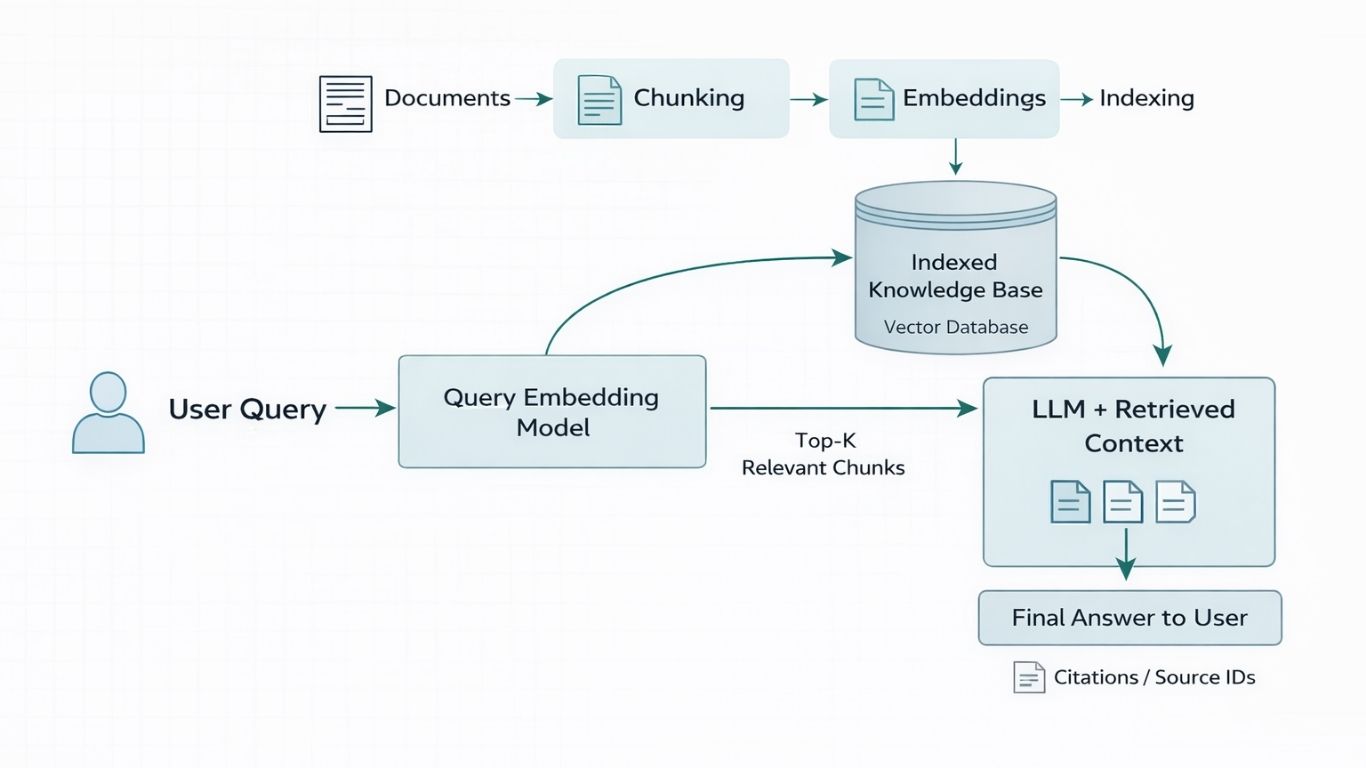
The choice of model here depends on your use case. GPT-4o is often preferred for complex reasoning tasks, while smaller models like Llama 3 offer faster, cost-effective alternatives. Crucially, you should configure the prompt to force the model to reference source document IDs. This allows the UI to display clickable footnotes, ensuring the RAG AI chatbot remains transparent and trustworthy.
Phase 4: Evaluation and Optimization
A RAG AI chatbot is not finished upon deployment. You must rigorously measure its accuracy using evaluation frameworks like Ragas or TruLens. These tools assess the “RAG Triad”:
-
Context Relevance: Did we find the right data?
-
Grounding: Is the answer supported by that data?
-
Answer Relevance: Did we actually answer the user?
Additionally, implementing feedback loops allows you to review retrieval logs, identify missing knowledge, and continuously refine your chunking strategies. This iterative process is key to maintaining a competitive edge.
CONTACT US FOR A FREE CONSULTATION
Accelerate Your AI Transformation with HBLAB
As detailed in this guide, constructing a robust RAG AI chatbot requires a sophisticated pipeline, from semantic chunking to precise vector retrieval. While the architecture is powerful, the engineering overhead to build it from scratch is significant.
At HBLAB, we bridge the gap between technical complexity and tangible business value.
With over 9 years of dedicated R&D and a portfolio of 50+ successful AI projects, HBLAB is more than a service provider; we are your strategic AI partner. Our team, featuring Top 0.5% Kaggle Experts and academic advisors, has encapsulated best-in-class RAG architecture into our proprietary solution: M-RAG.

M-RAG is engineered specifically to solve the challenges of enterprise knowledge retrieval.
It streamlines data ingestion across diverse document formats and utilizes a specialized “thinking mode” to process complex user queries with superior speed and accuracy. Most importantly, M-RAG mitigates the risk of hallucinations by ensuring every response is generated strictly from your verified source documents.
Beyond our products, we offer a “One Team” co-development model that integrates our 50+ AI specialists directly with your operations, reducing development costs by up to 40%. Whether you need to deploy M-RAG immediately or build a custom AI agent, HBLAB empowers your enterprise to move confidently into the AIX era.
FAQ
1. What is a RAG in chatbot?
In a chatbot context, RAG is the integration of a search engine mechanism with a generative text model. It allows the bot to “look up” information before speaking.
2. Is ChatGPT a RAG?
The base model of ChatGPT is not RAG; it relies on training data. However, when you use ChatGPT with “Browse with Bing” or Custom GPTs that have file uploads enabled, it functions as a rag ai chatbot.
3. Is there a 100% free AI chatbot?
Yes, platforms like HuggingChat and the free tiers of ChatGPT and Claude offer generative capabilities. However, building a custom rag ai chatbot for business usually incurs costs for hosting and API usage, though open-source tools like Ollama can reduce this expense.
4. What is an example of RAG in AI?
A corporate legal bot that searches through thousands of PDF contracts to answer specific questions about liability clauses is a prime example of a rag based ai chatbot.
5. What are the 4 levels of RAG?
The industry often categorizes these as Naive RAG (simple retrieval), Advanced RAG (pre/post-retrieval optimization), Modular RAG (specialized routing components), and Adaptive RAG (dynamically adjusting strategies based on query complexity).
6. What are the 7 types of RAGs?
Architectural variations include Standard RAG, Corrective RAG, Speculative RAG, Fusion RAG, Agentic RAG, Self RAG, and Graph RAG. Each type addresses specific accuracy or retrieval challenges.
7. What are the 4 models of AI?
The four fundamental types are Reactive Machines, Limited Memory, Theory of Mind, and Self-Awareness. Current LLMs and rag ai chatbot systems fall under Limited Memory.
8. What is LLM vs RAG?
An LLM is the reasoning engine and language generator. RAG is the architecture that gives the LLM access to external tools and data. RAG cannot exist without an LLM, but an LLM can exist without RAG.
Read more:
– Agentic AI In-Depth Report 2026: The Most Comprehensive Business Blueprint
– The Ultimate AI Agent Development Guide: Architecture, Tools, and The 6 Phase Framework
– Machine Learning – ML vs Deep Learning: Understanding Excellent AI’s Core Technologies


