Cloud computing deployment models explained—learn public, private, hybrid, and community cloud computing deployment strategies for your business. Complete guide with examples and comparison.
What Is Cloud Computing Deployment?
Understanding cloud computing deployment is essential for modern businesses. Cloud computing deployment refers to the architectural approach that determines how your infrastructure is allocated and managed in the cloud environment. More specifically, cloud computing deployment encompasses the four distinct models that organizations can choose from when implementing cloud services.
Think of cloud computing deployment as the blueprint that defines where your data lives, who controls it, and how you access it. In practical terms, cloud computing deployment determines whether your business infrastructure sits behind your own firewall, floats freely in a provider’s data center, or utilizes a combination of both environments.
The reality is clear: your cloud computing deployment choice affects everything—your monthly bills, your data security, your team’s operational workload, and your ability to scale. It’s arguably the first and most important decision you’ll make when implementing cloud services.
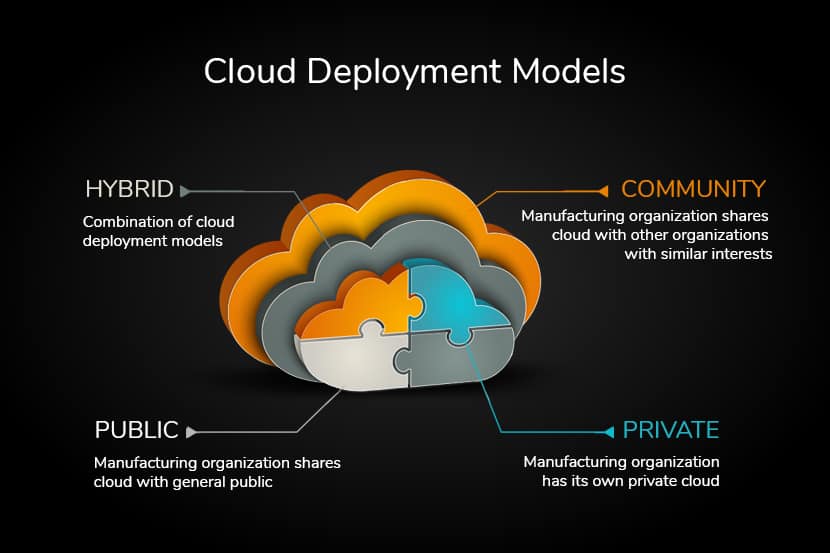
According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), cloud computing deployment consists of four primary models: public, private, community, and hybrid clouds. Each cloud computing deployment model reflects different types of cloud environments distinguished by ownership, scale, and access patterns. Understanding these cloud computing deployment options is crucial for selecting the right infrastructure strategy.
The Four Main Cloud Computing Deployment Models
1. Public Cloud Computing Deployment
Public cloud computing deployment occurs when a third-party cloud service provider—such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform—owns and operates the entire infrastructure. With public cloud computing deployment, you’re essentially renting computing power from them over the internet.
How Public Cloud Computing Deployment Works
In a public cloud computing deployment model, your resources are shared with other customers through multi-tenancy architecture. The cloud provider manages everything under cloud computing deployment scenarios: physical servers, networking, storage, security patches, and system updates. With public cloud computing deployment, you simply consume what you need and pay for exactly what you use.
Popular examples using cloud computing deployment principles include:
- Amazon EC2 and Amazon S3
- Microsoft Azure services
- Google App Engine
- Salesforce CRM platform
When to Choose Public Cloud Computing Deployment
Public cloud computing deployment shines when you need:
- Rapid scalability for unpredictable workloads—a key advantage of public cloud computing deployment
- Low upfront costs with pay-as-you-go pricing models in public cloud computing deployment
- Quick time-to-market for new applications through efficient cloud computing deployment
- Minimal infrastructure management overhead with managed cloud computing deployment services
Startups, SaaS companies, and organizations with seasonal demand typically benefit most from public cloud computing deployment strategies.
Advantages of Public Cloud Computing Deployment
✓ Cost-effective cloud computing deployment: No capital expenditure required; pay only operational expenses aligned with usage
✓ Instant scalability in cloud computing deployment: Add resources in minutes to handle traffic spikes through automated cloud computing deployment
✓ Global reach with cloud computing deployment: Access data centers across multiple regions via cloud computing deployment infrastructure
✓ Reduced management burden: Cloud computing deployment providers handle maintenance, updates, and compliance certifications
✓ Innovation access through cloud computing deployment: Use cutting-edge AI and machine learning tools without building them in cloud computing deployment
Disadvantages of Public Cloud Computing Deployment
✗ Limited control in cloud computing deployment: You can’t customize the underlying infrastructure with cloud computing deployment
✗ Security concerns with cloud computing deployment: Data sits alongside other customers’ data, requiring strong isolation and encryption in cloud computing deployment
✗ Compliance complexity: Meeting regulatory requirements in shared cloud computing deployment environments requires careful configuration
✗ Potential cost surprises in cloud computing deployment: High data egress fees or unpredictable usage patterns can inflate bills with cloud computing deployment
2. Private Cloud Computing Deployment
A private cloud computing deployment model represents infrastructure owned by a single organization. The infrastructure—servers, storage, networking—belongs exclusively to one entity. Whether it sits on-premises in your data center or off-premises at a dedicated hosting provider, only authorized users within your organization access private cloud computing deployment resources.
Understanding Private Cloud Computing Deployment Model
In a private cloud computing deployment scenario, you have complete ownership and control. Your IT team manages everything under private cloud computing deployment: security policies, infrastructure updates, and operational decisions. This private cloud computing deployment approach is ideal for organizations handling highly sensitive data or facing strict regulatory requirements.
Private cloud computing deployment comes in two variants:
- Internal Private Cloud Computing Deployment: Infrastructure housed in your organization’s own data center. This private cloud computing deployment approach offers maximum control but highest operational responsibility.
- External Private Cloud Computing Deployment: Infrastructure hosted by a third-party provider exclusively for your organization. This private cloud computing deployment model reduces management burden but provides less control than on-premises cloud computing deployment.
When to Use Private Cloud Computing Deployment
A private cloud computing deployment model makes sense when you need:
- Strict data control for intellectual property or customer information with private cloud computing deployment
- Compliance assurance in regulated industries through private cloud computing deployment
- Predictable performance without competition for resources in private cloud computing deployment
- Custom configuration for legacy applications requiring private cloud computing deployment
Financial institutions, government agencies, and healthcare organizations frequently choose private cloud computing deployment strategies.
Advantages of Private Cloud Computing Deployment
✓ Enhanced security with private cloud computing deployment: Only authorized personnel access your private cloud computing deployment infrastructure
✓ Full control with private cloud computing deployment: Customize every aspect to match your business processes within private cloud computing deployment
✓ Predictable performance in private cloud computing deployment: Resources aren’t shared; guaranteed capacity with private cloud computing deployment
✓ Compliance-friendly cloud computing deployment: Easier regulatory compliance with private cloud computing deployment approaches
✓ Data residency control through private cloud computing deployment: Keep sensitive information within specific geographic boundaries using private cloud computing deployment
Disadvantages of Private Cloud Computing Deployment
✗ High initial investment: Significant capital costs for hardware, software, and infrastructure with cloud computing deployment
✗ Ongoing operational complexity: Your team must handle maintenance, patching, and upgrades with private cloud computing deployment
✗ Slower scaling in private cloud computing deployment: Adding capacity takes weeks, not minutes with private cloud computing deployment
✗ Expertise required for cloud computing deployment: Need specialists in virtualization, networking, and cloud computing deployment management
✗ Limited flexibility with private cloud computing deployment: Scaling down is difficult when demand decreases with private cloud computing deployment
3. Hybrid Cloud Computing Deployment
Hybrid cloud computing deployment combines private and public cloud resources into a cohesive environment. With hybrid cloud computing deployment, some applications and data live on private infrastructure, while others run on public cloud services. Hybrid cloud computing deployment represents the “best of both worlds” approach to infrastructure management.
How Hybrid Cloud Computing Deployment Works
Imagine this hybrid cloud computing deployment scenario: Your organization processes sensitive customer payment data in a private cloud environment where security is paramount with cloud computing deployment. Simultaneously, you’re running analytics and machine learning workloads on AWS to leverage their capabilities. This represents hybrid cloud computing deployment in action.
Cloud computing deployment models like AWS Outposts, Azure Stack, and Google Anthos exemplify modern hybrid cloud computing deployment solutions, providing seamless integration between private and public cloud computing deployment environments.
When to Use Hybrid Cloud Computing Deployment
Hybrid cloud computing deployment is ideal when you’re:
- Migrating gradually from on-premises to public cloud through cloud computing deployment
- Balancing cost and control between different workload types with cloud computing deployment
- Managing regulatory requirements while exploiting cloud innovation through cloud computing deployment
- Ensuring disaster recovery across multiple cloud computing deployment environments
Most enterprises today operate some form of hybrid cloud computing deployment strategy.
Advantages of Hybrid Cloud Computing Deployment
✓ Flexibility with cloud computing deployment: Move workloads between private and public clouds based on needs through cloud computing deployment
✓ Cost optimization through cloud computing deployment: Keep expensive systems privately while using cheaper public cloud computing deployment for variable workloads
✓ Security balance with cloud computing deployment: Store sensitive data privately, leverage public cloud computing deployment for non-sensitive operations
✓ Scalability through cloud computing deployment: Public cloud provides burst capacity when private infrastructure reaches limits with cloud computing deployment
✓ Compliance friendly cloud computing deployment: Meet regulatory requirements while maintaining innovation velocity with cloud computing deployment
✓ Business continuity via cloud computing deployment: Applications failover between environments if one fails with cloud computing deployment
Disadvantages of Hybrid Cloud Computing Deployment
✗ Integration complexity with cloud computing deployment: Managing multiple platforms requires sophisticated networking and security with cloud computing deployment
✗ Higher costs: Maintaining both private and public infrastructure can be expensive with cloud computing deployment
✗ Operational overhead: Teams need expertise across multiple cloud computing deployment platforms
✗ Data consistency challenges in cloud computing deployment: Synchronizing data between environments adds complexity to cloud computing deployment
✗ Vendor lock-in risk with cloud computing deployment: Becoming dependent on multiple vendors’ proprietary tools in cloud computing deployment
4. Community Cloud Computing Deployment
Community cloud computing deployment is shared among several organizations with common goals, security requirements, or compliance needs. Think of community cloud computing deployment as a private cloud built for a group rather than a single entity.
Understanding Community Cloud Computing Deployment
Organizations in the same industry—healthcare providers, financial institutions, educational entities—often pool resources to create a community cloud computing deployment that addresses their shared concerns. The infrastructure under community cloud computing deployment is governed collaboratively, sometimes managed by one organization or a third-party provider.
When to Use Community Cloud Computing Deployment
Community cloud computing deployment suits:
- Industry consortiums sharing compliance requirements through cloud computing deployment
- Government agencies needing classified data sharing via cloud computing deployment
- Educational institutions collaborating on research with cloud computing deployment
- Financial networks requiring consistent security standards through cloud computing deployment
Advantages of Community Cloud Computing Deployment
✓ Reduced costs with community cloud computing deployment: Multiple organizations share infrastructure expenses through cloud computing deployment
✓ Tailored compliance through cloud computing deployment: Built specifically for industry requirements via cloud computing deployment
✓ Better security than public cloud: More control with community cloud computing deployment than public cloud computing deployment
✓ Collaborative capabilities through cloud computing deployment: Designed for inter-organizational data sharing with cloud computing deployment
Disadvantages of Community Cloud Computing Deployment
✗ Limited scalability with community cloud computing deployment: Resources are fixed based on community size in cloud computing deployment
✗ Governance challenges with cloud computing deployment: Decisions require consensus among multiple organizations using cloud computing deployment
✗ Inflexibility in cloud computing deployment: Changes need unanimous approval, slowing innovation with cloud computing deployment
✗ Limited applicability: Small organizations may find community cloud computing deployment irrelevant
Cloud Computing Deployment Models Diagram
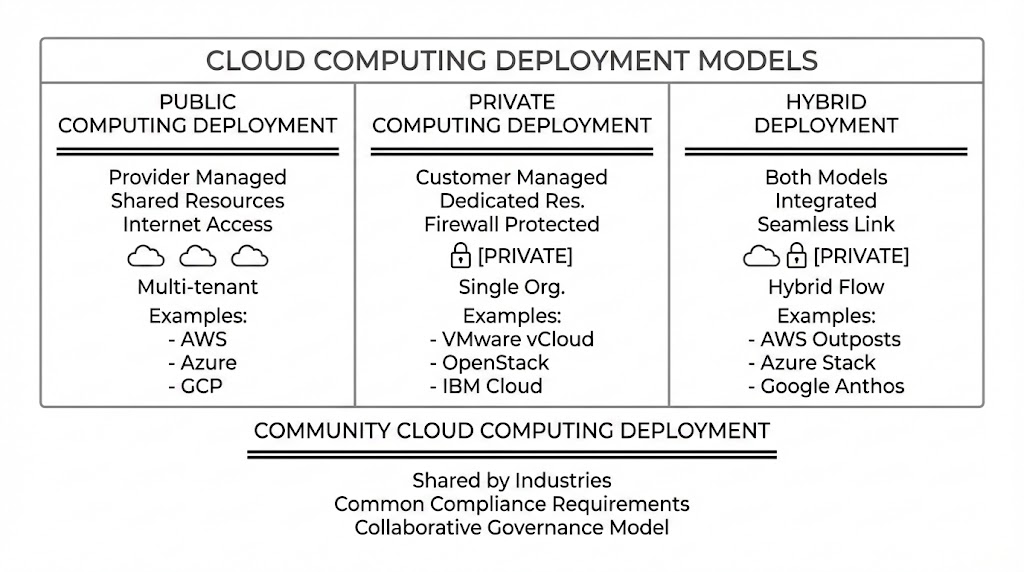
Cloud Computing Deployment vs. Service Models
- Cloud computing deployment models and cloud service models serve different purposes, though they work together harmoniously.
- Cloud computing deployment models answer: Where does my infrastructure live?
- Cloud service models answer: What level of control do I want?
Understanding Service Models Within Cloud Computing Deployment

- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Within cloud computing deployment strategies, you rent computing resources (servers, storage, networking). You manage applications, operating systems, and middleware while using cloud computing deployment.
Example IaaS with cloud computing deployment: AWS EC2, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): With cloud computing deployment, you rent a development platform. The provider manages infrastructure and operating systems. You focus on applications within your cloud computing deployment.
Example PaaS with cloud computing deployment: Google App Engine, Heroku, AWS Lambda
- Software as a Service (SaaS): You use ready-made applications delivered over the internet. You manage nothing except your data and user interactions within cloud computing deployment.
Example SaaS with cloud computing deployment: Salesforce, Microsoft 365, Google Workspace
You can deploy any service model on any cloud computing deployment model. For instance, you might use SaaS on public cloud computing deployment, while running IaaS applications on private cloud computing deployment. Both coexist in your hybrid cloud computing deployment strategy.
Key Factors When Selecting Your Cloud Computing Deployment Model
1. Cost Analysis in Cloud Computing Deployment
Public cloud computing deployment excels for variable, unpredictable workloads due to pay-as-you-go pricing. Private cloud computing deployment makes sense for consistent, long-running workloads with high utilization rates.
When analyzing cloud computing deployment costs, consider:
- Initial capital investment required for cloud computing deployment
- Ongoing operational expenses with cloud computing deployment
Hidden expenses in cloud computing deployment (data transfer, licensing) - Long-term cost trends with your cloud computing deployment
2. Security and Compliance in Cloud Computing Deployment
Different industries have different cloud computing deployment security needs. Healthcare (HIPAA), finance (PCI-DSS), and government (FedRAMP) have strict requirements often demanding private or hybrid cloud computing deployment.
Ask when selecting cloud computing deployment:
- What data sensitivity level do I have?
- What compliance standards apply to my cloud computing deployment?
- Can I meet requirements in shared cloud computing deployment environments?
3. Performance and Latency in Cloud Computing Deployment
Public cloud computing deployment offers global distribution with low latency. Private cloud computing deployment delivers predictable, consistent performance. Hybrid cloud computing deployment balances both approaches.
Consider for your cloud computing deployment:
- Geographic location of users requiring cloud computing deployment
- Performance requirements for cloud computing deployment
- Network latency tolerance for cloud computing deployment
- Real-time processing needs for cloud computing deployment
4. Scalability Needs with Cloud Computing Deployment
Public cloud computing deployment provides virtually unlimited elasticity. Private cloud computing deployment scales within purchased capacity. Hybrid cloud computing deployment offers both options.
Think about your cloud computing deployment:
- Expected growth trajectory requiring cloud computing deployment
- Peak vs. average usage patterns for cloud computing deployment
- Time required to add capacity with cloud computing deployment
- Seasonal fluctuations in your cloud computing deployment usage
5. Control and Customization in Cloud Computing Deployment
Private cloud computing deployment offers maximum control and customization. Public cloud computing deployment provides standardized environments. Hybrid cloud computing deployment provides flexibility.
Evaluate for your cloud computing deployment:
- How much infrastructure customization do you need for cloud computing deployment?
- Can you work within provider limitations in cloud computing deployment?
- Do you need specific hardware configurations for cloud computing deployment?
6. Operational Expertise Required in Cloud Computing Deployment
Public cloud computing deployment requires less internal expertise. Private cloud computing deployment demands substantial IT knowledge. Hybrid cloud computing deployment needs both.
Assess your cloud computing deployment team:
- What skills does your team have for cloud computing deployment?
- Can you hire or train for specific cloud computing deployment expertise?
- What’s the cost of hiring specialized cloud computing deployment talent?
Cloud Computing Deployment Models Comparison Table
| Aspect | Public Cloud | Private Cloud | Hybrid Cloud | Community Cloud |
| Ownership | Third-party provider | Single organization | Mixed | Multiple organizations |
| Setup Complexity | Simple | Complex | Very complex | Complex |
| Initial Cost | Minimal | Very high | High | Moderate |
| Ongoing Cost | Variable | Fixed (high) | Mixed | Distributed |
| Scalability | Unlimited | Limited | Very high | Limited |
| Security Level | Good (shared) | Excellent | Excellent | Good |
| Control Level | Low | Complete | High | Shared |
| Compliance | Variable | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
| Performance | Good | Excellent | Excellent | Good |
| Best For | Startups | Enterprise, Finance | Large enterprises | Industry groups |
Why Hybrid Cloud Computing Deployment Is Growing
Hybrid cloud computing deployment is increasingly popular because it acknowledges reality: enterprises rarely have one-size-fits-all cloud computing deployment needs.
The typical cloud computing deployment journey looks like this:
- Start with public cloud computing deployment – Speed and cost efficiency in cloud computing deployment
- Add private cloud computing deployment – Control for sensitive systems requiring cloud computing deployment
- Create hybrid cloud computing deployment – Balance across your organization’s cloud computing deployment
- Consider multicloud cloud computing deployment – Best-of-breed services from different providers via cloud computing deployment
Organizations using hybrid cloud computing deployment strategies report:
- 30% better cost optimization through workload placement in cloud computing deployment
- Faster compliance achievement in regulated industries via cloud computing deployment
- Improved disaster recovery capabilities with cloud computing deployment
- Greater flexibility responding to business changes through cloud computing deployment
- Reduced vendor lock-in from strategic cloud computing deployment
Common Mistakes When Selecting Cloud Computing Deployment Models
Mistake 1: Ignoring Compliance Early in Cloud Computing Deployment
Many organizations choose public cloud computing deployment first, then discover later that compliance requirements demand private cloud computing deployment infrastructure. Redesigning architecture mid-stream costs 5-10x more than planning cloud computing deployment properly.
Fix: Audit compliance requirements before selecting cloud computing deployment models.
Mistake 2: Underestimating Operational Costs in Cloud Computing Deployment
Initial cloud computing deployment costs look cheap until you factor in: data transfer fees, security tools, compliance monitoring, and management overhead for cloud computing deployment.
Fix: Model total cost of ownership across 3-5 years for cloud computing deployment.
Mistake 3: Overlooking Data Gravity in Cloud Computing Deployment
Data egress fees from public cloud computing deployment can be substantial. Moving terabytes of data between cloud computing deployment providers is expensive and slow.
Fix: Consider where data will live when choosing cloud computing deployment models.
Mistake 4: Forgetting About Vendor Lock-In with Cloud Computing Deployment
Public cloud computing deployment providers offer proprietary services that work beautifully together but are difficult to migrate away from in cloud computing deployment.
Fix: Design cloud computing deployment models with exit strategies and avoid unnecessary proprietary services.
Mistake 5: Not Planning for Hybrid Cloud Computing Deployment Initially
Attempting to retrofit hybrid cloud computing deployment integration after deploying separate public and private cloud computing deployment systems is expensive and complex.
Fix: If hybrid is your future cloud computing deployment goal, architect for it from the beginning.
The Future of Cloud Computing Deployment

The cloud computing deployment landscape is evolving. New approaches emerging include:
- Distributed Cloud Computing Deployment: Cloud services deployed closer to users at edge locations, reducing latency for IoT and real-time applications requiring cloud computing deployment.
- Green Cloud Computing Deployment: Deployment models optimizing energy consumption through efficient resource utilization and smart workload placement in cloud computing deployment.
- Serverless Cloud Computing Deployment: Abstraction layers that eliminate infrastructure concerns for certain workloads using cloud computing deployment.
- Edge-Cloud Hybrid Deployment: Combining edge computing with cloud computing deployment models for real-time processing with cloud scalability.
These innovations don’t replace traditional cloud computing deployment models—they extend and enhance cloud computing deployment capabilities.
Making Your Cloud Computing Deployment Decision
Start with these steps for cloud computing deployment:
Step 1: Audit Your Workloads for Cloud Computing Deployment
- List all applications and data stores requiring cloud computing deployment
- Classify by sensitivity: public, internal, restricted for cloud computing deployment
- Identify compliance requirements for each cloud computing deployment scenario
Step 2: Evaluate Requirements Per Workload in Cloud Computing Deployment
- Performance needs (latency, throughput) for cloud computing deployment
- Security requirements for cloud computing deployment (encryption, access control)
- Compliance mandates (HIPAA, PCI-DSS, GDPR) for cloud computing deployment
- Growth projections and scaling needs for cloud computing deployment
Step 3: Model Cost Scenarios for Cloud Computing Deployment
- Public cloud computing deployment for variable workloads
- Private cloud computing deployment for consistent, high-utilization workloads
- Hybrid cloud computing deployment for mixed portfolios
Step 4: Start Small, Iterate with Cloud Computing Deployment
- Begin with non-critical workloads in cloud computing deployment
- Learn what works for your organization’s cloud computing deployment
- Expand gradually as you build cloud computing deployment expertise
Step 5: Build a Migration Roadmap for Cloud Computing Deployment
- Define phases for moving workloads through cloud computing deployment
- Plan for integration challenges in cloud computing deployment
- Budget for tools and expertise required for cloud computing deployment
Conclusion: Cloud Computing Deployment as Strategic Infrastructure
Your cloud computing deployment choice isn’t just a technical decision—it’s a strategic one affecting security, cost, innovation velocity, and competitive advantage through cloud computing deployment.
Public cloud computing deployment excels for growth and innovation. Private cloud computing deployment provides control and compliance. Hybrid cloud computing deployment offers flexibility. Community cloud computing deployment enables industry collaboration.
The future likely belongs to organizations that thoughtfully combine multiple cloud computing deployment models—using each where it performs best, not deploying everything to the cloud environment just because it’s trendy.
Start by understanding your specific cloud computing deployment needs. Audit workloads systematically for cloud computing deployment. Model costs realistically for cloud computing deployment. Then choose your cloud computing deployment model strategy deliberately.
The right cloud computing deployment model for your organization might be public, private, hybrid, or community cloud computing deployment. What matters is that you’ve made an informed choice aligned with business objectives through proper cloud computing deployment planning.
Your cloud computing deployment journey starts with one clear question: Where do my applications and data need to live? Answer that honestly, and the rest of your cloud computing deployment decision becomes much clearer.
Quick Reference: Cloud Computing Deployment Models Summary
Public Cloud Computing Deployment: Provider-owned, internet-accessible, pay-as-you-go model ideal for startups and variable workloads using cloud computing deployment.
- Private Cloud Computing Deployment: Organization-owned, controlled infrastructure, high cost, ideal for regulated industries and sensitive data requiring cloud computing deployment.
- Hybrid Cloud Computing Deployment: Public + Private combined in balanced approach, growing choice for enterprises managing mixed portfolios via cloud computing deployment.
- Community Cloud Computing Deployment: Shared by similar organizations, cost-efficient cloud computing deployment ideal for industry consortiums.
Choose your cloud computing deployment model based on cost, security, compliance, scalability, and control needs—not marketing hype.
About HBLAB
HBLAB – Your Trusted Cloud Engineering Partner: Choosing the right cloud computing deployment models (public, private, hybrid, or community) is only the first step—execution requires solid architecture, secure implementation, and reliable operations.
With 10+ years of experience and a team of 630+ professionals, HBLAB helps organizations design and implement cloud solutions that match the right deployment model for each workload—covering cloud-native application development, cloud migration, DevOps automation, and security-by-design practices aligned to enterprise needs.

HBLAB holds CMMI Level 3 certification for disciplined delivery and quality processes, and has been building AI-powered solutions since 2017, which is useful when modern cloud programs include automation, observability, and intelligent operations.
With flexible engagement models (offshore, onsite, dedicated teams) and cost-efficient delivery (often ~30% lower cost), HBLAB can support everything from a single cloud assessment to full-scale hybrid deployment execution.
👉 Looking for a partner to implement the right cloud computing deployment model and scale it securely?
FAQ
1. What are the 4 cloud deployment models?
The four cloud computing deployment models are public, private, hybrid, and community.
2. What are the different cloud deployments?
“Different cloud deployments” usually refers to the same four cloud computing deployment models: public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, and community cloud.
3. What is the NIST model of cloud computing?
In NIST terminology, the main cloud computing deployment models are public, private, hybrid, and community, describing ownership and access patterns for cloud environments.
4. What are the 4 types of clouds in cloud computing?
The “4 types of clouds” in cloud computing typically means the four cloud computing deployment models: public, private, hybrid, and community.
5. What are the 4 cloud service models?
Cloud service models are commonly IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, and many add a fourth such as FaaS/serverless—these are different from cloud computing deployment models.
6. Which cloud model is most secure?
Among cloud computing deployment models, the private model is often considered most secure for strict control because access is limited to one organization, but security still depends on configuration and operations.
7. What is the most popular cloud model?
Across cloud computing deployment models, public cloud is often the most common entry point for speed and scalability, while many enterprises operate hybrid cloud computing deployment models long-term.
8. Which is more secure, AWS or Azure?
AWS vs Azure security is usually determined by how identity, network controls, encryption, and monitoring are implemented, regardless of the chosen cloud computing deployment models.
9. What are the 5 pillars of cloud security?
A practical five-part view is: identity & access, data protection, workload protection, visibility/detection, and governance/compliance—applied consistently across all cloud computing deployment models.
10. What are the 4 C’s of cloud security?
A common 4C checklist is configuration, controls, compliance, and continuity—again applied across cloud computing deployment models.
11. What are the 5 pillars of AWS?
The AWS Well-Architected pillars are operational excellence, security, reliability, performance efficiency, and cost optimization, and they guide design choices across cloud computing deployment models.
13. What are the 5 C’s of cyber security?
There is no single universal “5C” standard, but some teams use a simple 5C mnemonic (coverage, controls, compliance, continuity, culture) to ensure security practices remain consistent across cloud computing deployment models.
Read More:
– Data Integration in 2025: The Complete Guide to Unified Data Solutions
– Cloud Network Security: Complete Guide to Secure Cloud Networking in 2025
– AWS Singapore: Essential 2026 Guide to Data Centers, Costs and MAS Compliance




