Will AI replace doctors? With the global healthcare AI market projected to reach $110.61B by 2030, the question will AI replace doctors continues to spark debates among medical professionals and tech innovators.
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing healthcare, enhancing diagnostics and patient care, but can it fully supplant the human touch of physicians?
This article dives into whether AI will replace doctors, exploring AI-driven healthcare solutions, real-world applications, and how HBLAB’s expertise in AI in healthcare empowers organizations to navigate this transformation.
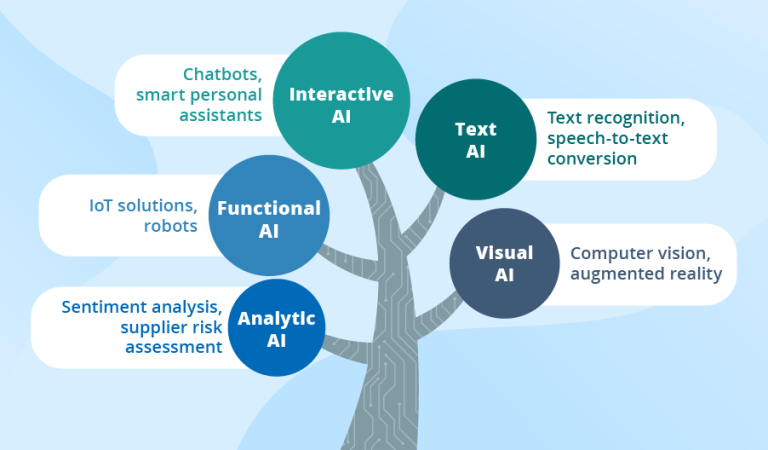
What is AI in Healthcare?

AI in healthcare refers to the use of advanced algorithms and machine learning to analyze medical data, improve diagnostics, and enhance patient care. It encompasses applications like predictive analytics, robotic surgery, and virtual health assistants. Sub-terms like AI-driven medical diagnostics and AI-assisted patient care highlight its growing influence in streamlining processes while supporting doctors.
AI systems process vast datasets—such as medical imaging or patient records—faster and with greater accuracy than humans in specific tasks. For instance, AI can detect anomalies in X-rays with 95% accuracy. However, it lacks the emotional intelligence and holistic judgment doctors provide.
HBLAB has an in-depth study on the importance of Agentic AI — Read more now
Real Stories: Doctors, Patients, and AI’s Role
Step into a hospital room or an online forum, and you’ll hear one question: Will AI replace doctors? From Reddit threads to Quora debates, real stories of patients and physicians reveal how AI in healthcare is reshaping care—not by sidelining humans, but by amplifying their impact.
A Cancer Survivor’s Journey with AI
Sarah, a 42-year-old cancer survivor, clutching her treatment plan in a dimly lit clinic. On Reddit, she shared how an AI medical chatbot analyzed her complex chemotherapy regimen in seconds, flagging alternative options her oncologist hadn’t considered. This AI-driven healthcare solution empowered her to ask bold questions, but it was her doctor’s warm reassurance—“You’re stronger than this disease”—that gave her hope.
Adopt AI-assisted patient care to give your patients confidence without losing the human touch.
An ER Doctor’s Race Against Time
Dr. Chen in a bustling ER, swamped with patient data during a hectic night shift. On Quora, he described how AI-driven medical diagnostics detected pneumonia patterns in chest X-rays with 79% accuracy (University of Nottingham), saving precious minutes. Yet, he noted that AI will not replace doctors—it missed a patient’s subtle wince, a clue to a rare allergic reaction only his years of experience caught.
Invest in scalable AI healthcare solutions to streamline diagnostics while preserving clinical intuition.
A Pediatrician’s Healing Smile
Dr. Maya, a pediatrician, kneeling beside a frightened six-year-old before a tetanus shot. A Reddit post recounted her asking, “What’s your favorite cartoon?”—a moment no AI medical chatbot could replicate. While AI in healthcare excels at data crunching, AI will not replace doctors in delivering empathy that soothes young patients.
Use AI-assisted patient care to free clinicians for these irreplaceable human connections.
A Surgeon’s Creative Precision
Step into the operating theater with Dr. Patel, guiding a robotic arm through a delicate procedure. On Quora, he explained how AI-driven healthcare solutions enable pinpoint accuracy in surgeries, like removing a bullet with minimal tissue damage. But when a sportsperson’s wound required immediate stitching versus medication for a retiree, his creative judgment proved AI will not replace doctors.
Leverage precision medicine with AI to enhance surgical outcomes while relying on human expertise.
A Rural Nurse’s Lifeline
Meet Nurse Aisha in a remote clinic, where specialists are hours away. She shared on Reddit how an AI-driven healthcare solution predicted Alzheimer’s risk in a patient six years early with 100% accuracy (Kaggle competition data). Yet, she needed to hold the patient’s hand to explain the diagnosis, proving AI will not replace doctors in delivering life-changing news.
Implement scalable AI healthcare solutions to bridge gaps in underserved regions.
Patients’ Trust in Human Care
Listen to patients debating will AI replace doctors on Quora. A tech-savvy 30-year-old praised AI medical chatbots for cutting lab report wait times from days to minutes, boosting efficiency. But an elderly patient insisted on a doctor’s empathetic guidance for a heart condition, showing AI healthcare challenges in replicating trust.
Balance efficiency and empathy with AI-assisted patient care in your healthcare systems.
The Power of Partnership
These stories echo a universal truth: AI will not replace doctors, but it will redefine their roles.
A Reddit user declared, “Doctors using AI-driven healthcare solutions will outshine those who don’t.”
👉 Join the AI revolution with HBLAB’s expertise—contact us for a free consultation!
How AI works in HealthCare
No — Will AI Replace Doctors? The answer is No; AI in healthcare augments clinicians by delivering faster insights, automating routine work, and surfacing risks earlier, while medical decisions and accountability remain with doctors. Put simply, the question “Will AI Replace Doctors” misunderstands the goal: AI is built to assist clinicians, not to replace them.
How it works (plain view)
AI in healthcare works by connecting clinical data pipelines to models and feeding results back into everyday clinical workflows with safety guardrails, so the debate “Will AI Replace Doctors” shifts toward “How does AI help doctors do more, safely?” AI integrates with existing systems instead of acting alone, ensuring doctors stay in control from start to finish.
Data collection
Healthcare data flows through standards like HL7/FHIR for EHR data and DICOM for medical images, letting AI read only what’s needed (e.g., Patient, Observation, Medications) and write results back in a traceable way. When people ask, “Will AI Replace Doctors,” this standardization shows why not: doctors orchestrate care while AI securely delivers the right data at the right time.
Imaging moves from scanners to PACS using DICOM, and AI services “subscribe” to new studies, analyze them, and return triage flags or measurements right inside the radiologist’s viewer. Again, Will AI Replace Doctors? No—the radiologist reviews and signs off; AI just accelerates pattern recognition and quantification.
👉 Get our in-depth IT communication guide now—free to download.
Wearables add patient‑generated data (e.g., heart rhythm, activity) as structured Observations, so clinicians can follow up on alerts with confirmatory tests. When considering Will AI Replace Doctors, remember wearables don’t diagnose; they prompt clinicians to evaluate sooner.
Analysis and insights
Models turn inputs into features and produce classifications or risk scores, using deep learning for images and structured ML for EHR tables. Will AI Replace Doctors at this stage? No—human‑AI collaboration consistently performs best, with clinicians validating AI suggestions and deciding next steps.
In stroke triage, AI flags suspected large‑vessel occlusions on CT and pings the on‑call team, cutting minutes off door‑to‑treatment. Will AI Replace Doctors here? It can’t—only specialists decide on thrombectomy and manage complications; AI just reduces time to action.
For early deterioration (like sepsis), prospectively validated models trigger earlier evaluations and care bundles. Will AI Replace Doctors in these scenarios? No—AI elevates signal; clinicians interpret context, comorbidities, and patient goals to act appropriately.
NLP and LLM copilots help find guidelines, summarize records, and draft notes—but they can hallucinate—so outputs are reviewed and signed by clinicians. That’s why the practical answer to Will AI Replace Doctors is still no; oversight is required by design.
Implementation in workflow
Inside the EHR, CDS Hooks call an external service when a clinician opens a chart or signs an order and return “cards” with next‑best actions directly in the workflow. This reduces clicks and keeps decision support visible without interrupting care, reinforcing that “Will AI Replace Doctors” is the wrong frame—AI is embedded to guide, not to override.
In imaging, AI services ingest DICOM exams, compute results, and send structured findings back to PACS/EHR, where specialists review and finalize. With clinical documentation, ambient AI drafts notes from conversations, but clinicians edit and attest, ensuring authorship and medical responsibility remain human—another reason “Will AI Replace Doctors” remains a myth.
Administrative automation (RPA) handles high‑volume, rules‑based tasks like appointment reminders or prior auth checks, freeing staff for patient‑facing work. This kind of automation makes care teams more available; it doesn’t answer “Will AI Replace Doctors” so much as “How does AI give time back to doctors?”
Feedback loop and safety
AI updates are governed and tested before rollout, not “self‑learning” on live patients. Regulators now allow predefined, controlled model updates (with data, validation, and monitoring plans), proving that the system assumes doctors are in charge and asks AI to earn trust over time—not to replace clinicians.
Post‑market monitoring checks for performance drift, fairness, and safety issues; results are audited and models retrained or rolled back as needed. Global guidance also requires transparency, human oversight, and incident reporting—further evidence that the real question isn’t “Will AI Replace Doctors,” but “How does AI help doctors deliver safer, faster, fairer care?”
Bottom line on “Will AI Replace Doctors”
The practical answer to “Will AI Replace Doctors” is a firm no: AI is a clinical copilot that standardizes data access, accelerates detection, and automates paperwork while keeping clinicians responsible for diagnosis, consent, and treatment. As systems evolve, the winning models make doctors more effective and compassionate—not obsolete.
Advantages of AI in Healthcare
AI offers transformative benefits for healthcare systems worldwide:
- Improved Diagnostic Accuracy: AI algorithms, like those used in AI-driven medical diagnostics, detect conditions such as cancer with up to 98% precision (Google Health).
- Cost Efficiency: Automating tasks like medical coding reduces operational costs by 20-30% (Gartner).
- Scalability: AI-assisted patient care enables hospitals to manage higher patient volumes without compromising quality.
- Personalized Medicine: AI tailors treatments based on individual patient data, improving outcomes.
- Time Savings: AI streamlines administrative tasks, freeing doctors to focus on patient care.
These advantages make AI in healthcare a powerful tool for enhancing efficiency and outcomes.
🌐 Don’t miss out—download our exclusive IT & AI playbook for 2025 and beyond.
Challenges and Risks of AI in Healthcare
Despite its potential, AI in healthcare faces significant challenges:
- Ethical Concerns: Bias in AI algorithms can lead to misdiagnoses, particularly for underrepresented groups.
- Data Privacy: Handling sensitive patient data raises compliance issues under regulations like HIPAA.
- Lack of Emotional Intelligence: AI cannot replicate the empathy and trust patients seek from doctors.
- Integration Barriers: Implementing AI-driven healthcare solutions requires significant investment and training.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Strict medical regulations slow AI adoption in clinical settings.
Addressing these AI healthcare challenges is critical to ensuring safe and effective implementation.
Collaboration, Not Competition: The Doctor-AI Partnership
Rather than asking will AI replace doctors, the focus should be on collaboration.
AI in healthcare excels in diagnostics, predictive modeling, and automation, freeing doctors for complex tasks like counseling.
For example, AI-driven medical diagnostics highlight tumors in imaging, but doctors validate findings using clinical judgment. This “human-in-the-loop” approach ensures efficiency without sacrificing trust.
Repetitive tasks like scheduling or triaging are shifting to AI-assisted patient care, allowing doctors to prioritize patient interaction.
Ethical and Legal Dilemmas in AI Medicine
The question will AI replace doctors raises ethical and legal concerns. Who is liable if AI-driven medical diagnostics err? Bias in training data, like inaccuracies in pulse oximeters for darker skin tones, risks disparities in AI in healthcare. Privacy is critical, as AI-assisted patient care processes sensitive data, requiring compliance with laws like HIPAA. Clear frameworks for accountability and consent are essential to maintain trust in scalable AI healthcare solutions.
HBLAB’s CMMI Level 3 certification ensures secure, ethical AI development for healthcare.
👉 Contact HBLAB for compliant AI solutions!
Role of Emerging Technologies in AI in Healthcare
Emerging AI technologies—especially machine learning, NLP, RPA, and generative AI—are transforming diagnostics, patient engagement, hospital operations, and the trajectory of precision medicine while global experts emphasize responsible governance to realize benefits safely and equitably.
Machine learning
Diagnostic accuracy: Systematic and narrative reviews report that ML and deep learning enhance image interpretation, reduce error rates, and streamline radiology workflows across modalities such as X‑ray, CT, MRI, and mammography, improving sensitivity/specificity and triage speed in clinical practice. Controlled deployments also suggest human‑AI collaboration can raise detection performance on chest radiography, reinforcing ML’s role as an augmentative tool rather than a replacement for clinicians.
Sepsis prediction and outcomes: A Nature Digital Medicine multi‑site study found deployment of the COMPOSER deep learning model for early sepsis prediction was associated with significant reductions in mortality and length of stay, evidencing real‑world clinical impact beyond retrospective AUCs. Meta‑analytic evidence likewise indicates ML models (notably neural networks and decision trees) outperform traditional scores for sepsis prediction, highlighting the need for rigorous validation and standardized reporting in diverse settings.
Outbreak and public health surveillance: Expert analyses and case evidence show AI‑enabled systems like BlueDot flagged COVID‑19 risks days before official alerts and previously forecast Zika spread months in advance by fusing NLP, mobility, and epidemiologic signals, illustrating how ML can augment early warning and situational awareness for infectious disease threats. Such platforms use large‑scale, multilingual data ingestion and probabilistic modeling to anticipate potential spread patterns and prioritize responses.
NLP and AI assistants
Use cases and governance: WHO’s 2024 guidance outlines five broad LLM applications in health—clinical decision support, patient‑guided information seeking, clerical/EHR tasks, education/simulation, and research/drug development—while calling for transparency, post‑deployment auditing, and rights‑preserving safeguards to mitigate risks like bias, privacy breaches, and misinformation. European regulators similarly published principles for safe, responsible use of LLMs in medicines regulation, reinforcing a convergent global emphasis on accountability and reliability.
Clinical documentation and chatbots: Real‑world studies of ambient scribing (e.g., Nuance DAX) show statistically significant but modest per‑encounter documentation time reductions with mixed effects on after‑hours EHR time, indicating workflow fit and operational design strongly influence outcomes. Practitioner reports describe improved note closure and satisfaction with advanced copilots, but expert reviews stress that LLMs still face hallucination and grounding limitations, requiring careful evaluation before patient‑facing chatbot deployment.
RPA in hospital operations
Efficiency and savings: Health systems report substantial administrative gains from RPA in scheduling, documentation, revenue cycle, and back‑office workflows—such as Singapore General Hospital saving over 50,000 staff hours and roughly $1.8 million in productivity since 2020 by automating high‑volume tasks. Large U.S. systems like Mass General Brigham have credited intelligent automation with returning 271,000 hours to staff and achieving about $10 million in savings, demonstrating enterprise‑level ROI at scale.
Scalable automation models: Regional authorities (e.g., Helse Vest in Norway) have centralized RPA teams to reuse automations across hospitals, achieving six‑figure annual savings (e.g., ~NOK 5 million in postage) and faster rollouts compared to traditional integrations, which strengthens clinical buy‑in and operational resilience. Targeted case work shows RPA can also clear massive data backlogs and reduce appointment no‑shows via automated notifications and rescheduling, translating to significant cost avoidance in weeks, not years.
Generative AI and precision medicine

Foundations and applications: Expert reviews in digital medicine describe how generative models synthesize medical text and multimodal data, generate synthetic datasets for privacy‑preserving model training, and support tasks from imaging augmentation to trial simulation, accelerating research pipelines. Systematic evidence further indicates generative models can aid personalized care by improving drug response prediction, treatment effect estimation, biomarker discovery, and patient stratification—while flagging the need for rigorous validation and bias mitigation.
Clinical reasoning LLMs: Frontier medical LLM research (e.g., Med‑PaLM and successors) demonstrates marked gains on medical benchmarks and physician‑rated answer quality across multiple clinical axes, indicating movement toward expert‑level reasoning under controlled evaluations, though specialist oversight remains essential. Methodological critiques caution that LLMs can under‑cite or over‑generalize medical evidence, reinforcing the importance of grounding, retrieval, and human review in clinical contexts.
Risk, regulation, and scale
Ethical guardrails: WHO calls for independent auditing, human‑rights‑based oversight, and accuracy benchmarks for LMMs across clinical, administrative, and research workflows to ensure equitable benefit and to reduce harm from bias or privacy violations as adoption accelerates globally. EMA guidance on LLM usage in medicines regulation adds a regulatory lens for evidence assessment and safety, complementing institutional governance and MLOps practices in health systems.
Implementation realities: Expert commentary emphasizes rigorous post‑deployment monitoring, dataset transparency, and human‑in‑the‑loop review to address hallucinations, drift, and distribution shifts, ensuring systems remain safe and clinically reliable over time. Combining quality management with interoperability and process redesign is repeatedly cited as a prerequisite for sustainable value creation in AI‑enabled care delivery.
When to Use AI in Healthcare?
No — Will AI Replace Doctors? The practical answer is no; AI in healthcare works best as a clinical copilot that accelerates diagnostics, streamlines operations, and extends care access while decisions remain with clinicians. In other words, the question “Will AI Replace Doctors” should be reframed as “When does AI help doctors deliver safer, faster care?”
High‑volume diagnostics
-
Use when imaging and lab volumes are high and turnaround time affects outcomes; AI triages studies, flags critical findings, and standardizes quantification without replacing specialist judgment, reinforcing that “Will AI Replace Doctors” is not the right question for radiology workflows.
-
Strong fit for CT, MRI, X‑ray, pathology slides, and high‑throughput labs where minutes matter, with clinicians validating AI findings and signing reports, so “Will AI Replace Doctors” remains a myth in practice.
Remote patient monitoring
-
Use for continuous risk detection in chronic care and post‑discharge, where AI surfaces deteriorations from wearables and home devices for clinician review, not to replace clinicians.
-
Ideal for telemedicine and underserved regions; AI escalates signals while clinicians make calls—clear evidence that “Will AI Replace Doctors” is not the operating model.
Administrative automation
-
Use for high‑volume, rules‑based tasks (prior auth status checks, eligibility, claims edits, scheduling, referrals) to cut delays and reduce burnout while keeping clinical staff focused on patients.
-
Automation gives time back to care teams; it improves access and efficiency rather than answering “Will AI Replace Doctors,” which is the wrong frame for back‑office transformation.
Specialized research
-
Use to accelerate target discovery, trial design, and cohort selection; AI prioritizes hypotheses and simulates scenarios that help researchers move faster.
-
Gains like reduced cycle time do not imply “Will AI Replace Doctors”; instead, AI augments investigators and clinicians with stronger evidence faster.
When AI makes sense
-
Clear pain point: measurable bottlenecks in turnaround times, denial rates, or no‑shows—AI is justified when there is a defined KPI and governance.
-
Reliable data: interoperable EHR/imaging feeds and consented patient‑generated data; without clean inputs, the “Will AI Replace Doctors” debate is moot because AI won’t be safe or effective.
-
Human‑in‑loop: defined review, override, and auditing—precisely why “Will AI Replace Doctors” is not how modern deployments work.
Bottom line
-
Will AI Replace Doctors? No—deploy AI where it reduces time‑to‑insight, lowers costs, and scales access, while clinicians remain accountable for diagnosis, consent, and treatment.
-
For organizations facing talent shortages or cost pressures, AI in healthcare offers scalable lift across diagnostics, monitoring, and administration—without replacing doctors, but empowering them.
HBLAB – Your Partner in AI in Healthcare
HBLAB is a trusted leader in AI in healthcare, empowering organizations with cutting-edge solutions to address global healthcare challenges. With 630+ professionals, including 30% senior-level experts with over 5 years of experience, HBLAB delivers cost-effective AI solutions that are 30% lower than local rates.

Our CMMI Level 3 certification ensures process excellence, while our AI expertise since 2017—bolstered by partnerships like VNU’s Institute for AI—drives innovation.
HBLAB offers flexible engagement models, including offshore, onsite, and dedicated teams, tailored to your needs. Whether you’re scaling diagnostics or building AI medical chatbots, our team integrates seamlessly, ensuring data security and compliance.
From startups to enterprises, HBLAB accelerates healthcare innovation with scalable AI healthcare solutions.
👉 Contact HBLAB for expert AI-driven healthcare solutions today!
Conclusion
AI in healthcare is revolutionizing diagnostics, patient care, and operational efficiency, but it’s unlikely to fully replace doctors. While AI-driven medical diagnostics and AI-assisted patient care enhance accuracy and scalability, human empathy and judgment remain irreplaceable. By addressing challenges like ethics and integration, organizations can harness AI in healthcare to transform patient outcomes. HBLAB’s expertise makes it the ideal partner for navigating this evolution. 👉 Contact us for scalable AI healthcare solutions!
FAQ
Can a doctor be replaced by AI?
Will AI Replace Doctors? No—AI enhances diagnostics and automates routine tasks, but complex reasoning, empathy, ethics, and accountability keep clinical decisions in human hands; AI-driven medical diagnostics support physicians rather than substitute for them.
Which jobs can’t AI replace?
Will AI Replace Doctors or therapists? Roles centered on emotional intelligence, nuanced communication, hands-on procedures, and complex care coordination are resilient; AI in healthcare complements these roles instead of eliminating them.
Will GPT‑5 replace doctors?
Will AI Replace Doctors—even with GPT‑5? No; large models can summarize records, suggest options, and draft notes, but medicine requires physical exams, informed consent, risk–benefit judgments, and shared decision-making that remain human-led.
Are doctors at risk from AI?
Will AI Replace Doctors soon? No immediate replacement, but task shift is real: more oversight of AI outputs, patient communication, and complex cases, while routine documentation and screening become AI-assisted.
Can a GP be replaced by AI?
Will AI Replace Doctors in primary care? No; GPs manage undifferentiated symptoms, multimorbidity, and long-term relationships; AI medical chatbots assist triage and education, but holistic care and continuity stay with clinicians.
Will AI replace doctors in 5 years?
Will AI Replace Doctors in 5 years? No; regulation, clinical validation, liability, and workflow integration mean AI will scale as a copilot—speeding diagnostics and administration—while doctors remain accountable.
Can a gynecologist be replaced by AI?
Will AI Replace Doctors in OB/GYN? No; procedural expertise, surgical judgment, safeguarding, and trust are central; AI helps with imaging review, documentation, and scheduling, not with replacing specialist care.
Did Bill Gates say AI will replace doctors?
Will AI Replace Doctors according to Bill Gates? Commentary highlights AI’s transformative potential in healthcare, but claims of full replacement are overstated; the direction is augmentation, not substitution.
CONTACT US FOR A FREE CONSULTATION
Read more:
– AI in Ecommerce (2025): Extraordinary Trends Redefining Online Shopping Worldwide
– Agentic AI In-Depth Report 2025: The Most Comprehensive Business Blueprint
– Agentic Reasoning AI Doctor: 5 Extraordinary Innovations Redefining Modern Medicine